Transit Gateway GRE Tunneling in AWS Workflow
Introduction
Connecting to on-prem network over the GRE tunneling protocol in AWS is an alternative to IPsec. When GRE tunneling is used, Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Gateways interoperate directly with on-prem network devices over AWS Direct Connect.
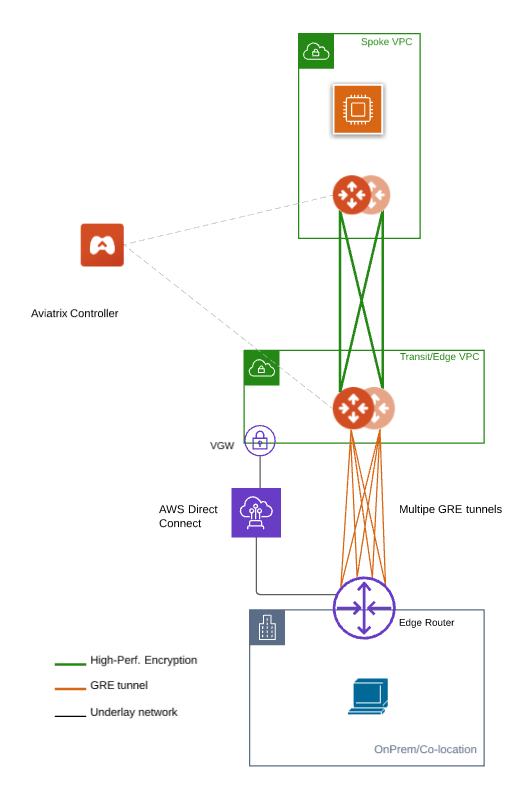
This diagram shows where Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Gateways connect to an on-prem edge router over Direct Connect.
This document provides step-by-step instructions on how to build Aviatrix Transit Gateway to External Device using GRE over AWS Direct Connect:
For more information about Multicloud Transit Network and External Device, refer to:
|
The key ideas for this solution are:
-
The edge (WAN) router runs a BGP session to AWS VGW via AWS Direct Connect where the edge router advertises its GRE IPs. AWS VGW advertises the AWS Transit VPC CIDR.
-
Leverage edge router BGP ECMP feature.
-
Configure multiple GRE tunnels for greater aggregate throughput.
|
Prerequisites
-
Upgrade Aviatrix Controller to the latest version.
-
In this example, we are going to deploy the below VPCs in AWS:
-
AWS Aviatrix Transit VPC (i.e. 10.1.0.0/16) by utilizing Aviatrix feature Create a VPC with Aviatrix FireNet VPC option enabled
-
AWS Aviatrix Spoke VPC (i.e. 192.168.1.0/24) by utilizing Aviatrix feature Create a VPC as the previous step or manually deploying it in each cloud portal. Moreover, feel free to use your existing cloud network.
-
-
Edge router has high throughput supported on hardware interface(s) and GRE tunnel(s)
Building Underlay Connectivity with AWS Direct Connect
Building AWS Direct Connect is your responsibility. For more information about AWS Direct Connect, please see Connect Your Data Center to AWS.
Adjust the topology depending on your requirements.
Building AWS Direct Connect
See Equinix ECX Fabric AWS Direct Connect if you select an Equinix solution. This is just an example. Make sure to select 10 Gbps capacity.
Associating AWS VGW to AWS Transit VPC
-
Log in to the AWS VPC Portal and select Virtual Private Gateways under the Virtual Private Network (VPN) sidebar.
-
Select the Virtual Private Gateway that you have the private virtual interface to AWS Direct Connect
-
Click Actions.
-
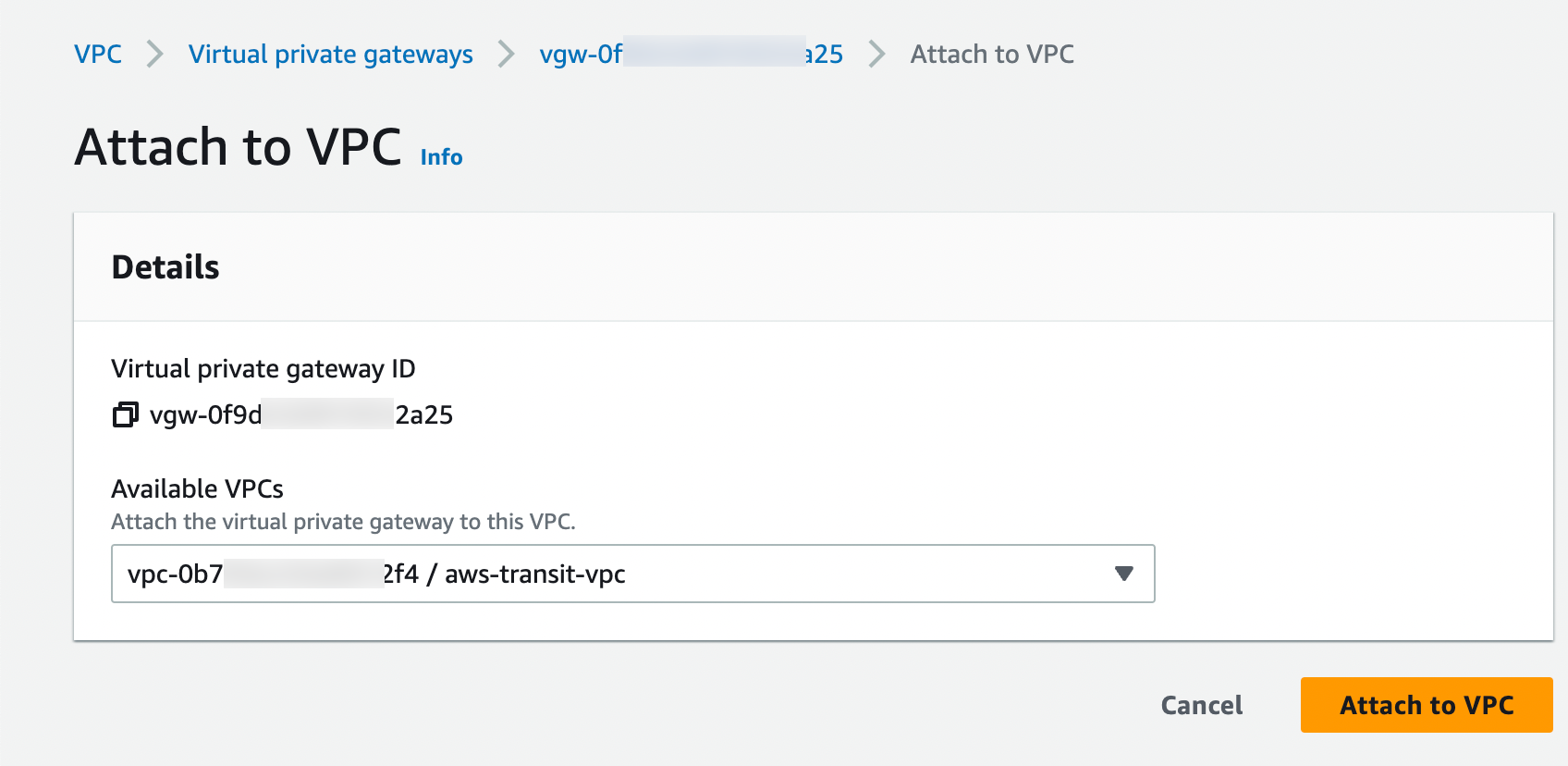
Select Attach to VPC.
-
Select the AWS Transit VPC and click Attach to VPC.
Deploying the Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Solution
Refer to Single Region Transit Network Workflow Instructions for the steps below. Please adjust the topology depending on your requirements.
Step 2.1. Deploy Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Gateway and HA in AWS
-
Follow this step to Deploy the Aviatrix Transit Gateway to launch Aviatrix Transit gateway and enable HA with insane mode enabled in the AWS Transit VPC.
-
In this example, sizes c5n.2xlarge and c5n.4xlarge are selected to benchmark performance.
Enabling Route Propagation on the Subnet Route Table where Aviatrix Transit Gateway Locates on AWS Portal
-
Log in to the AWS VPC portal and locate the subnet route table where the Aviatrix Transit Gateway is located.
-
Select Route Propagation tab.
-
Click Edit route propagation.
-
Locate the AWS VGW that is associated with this Transit VPC and mark the Propagate checkbox.
-
Click Save.
-
Check that the Propagate status is Yes.
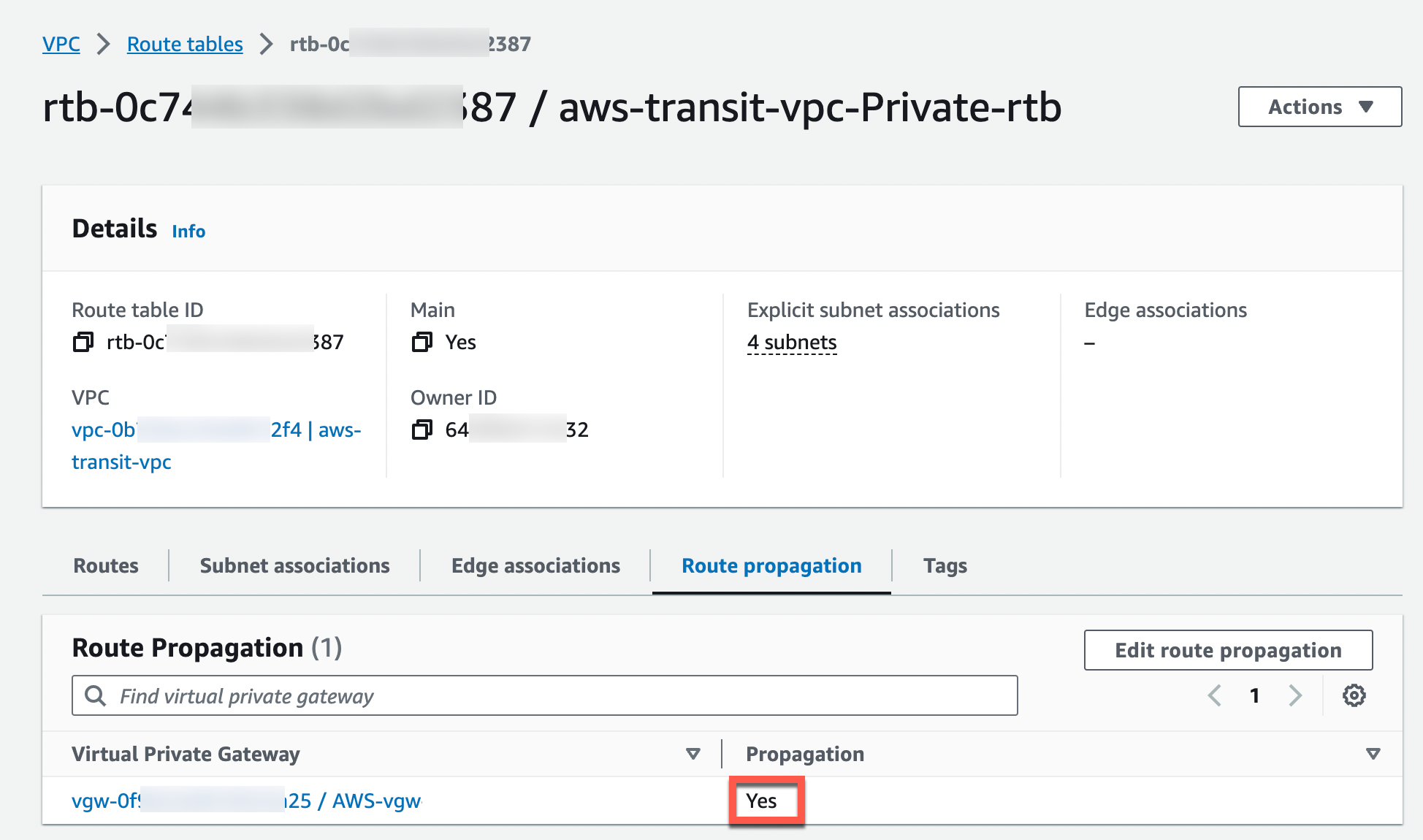
If the Propagation status is not Yes, you can enable it by clicking Edit route propagation.
Deploying Spoke Gateway and HA
Deploy Spoke Gateways to launch Aviatrix Spoke gateway and enable HA with insane mode enabled in AWS Spoke VPC.
In this example, sizes c5n.2xlarge and c5n.4xlarge are selected to benchmark performance.
Building Connectivity between Edge Router and Aviatrix Transit Gateway
Cisco ASR is used as an edge router in this example.
Checking Whether the edge router has Learned AWS Transit VPC CIDR via the BGP Session Between Edge Router and AWS Direct Connect
-
Log in to the edge router (i.e. Cisco ASR).
-
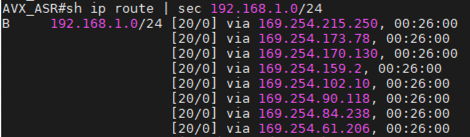
Check whether edge router has learned AWS Transit VPC CIDR via the BGP session between edge router and AWS Direct Connect by issuing the related "show ip bgp" command.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#show ip bgp
Preparing IP for GRE source IP on Edge Router
In this example, we use ASR loopback interface with an unique IP address as a GRE source IP.
Create a loopback interface and assign an IP to itself as a GRE source IP.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#interface Loopback77 (config-if)#ip address 192.168.77.1 255.255.255.255
Advertising that GRE source IP on Edge Router to the BGP Session Between Edge Router and AWS Direct Connect
The purpose of this step is to let AWS VGW learn the GRE source IP on edge router via BGP session between the edge router and AWS Direct Connect, so that the Aviatrix Transit Gateway can reach the GRE source IP on edge router to form a GRE tunnel over AWS Direct Connect.
To demonstrate this concept, we utilize IOS "ip prefix-list" function and apply it on BGP neighbor with direction out function to distribute GRE source IP.
Create a prefix list that defines GRE source IP on edge router for BGP advertisement.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#ip prefix-list Router-to-VGW description Advertised GRE source CIDRs 192.168.77.X/32 to build GRE tunnels (config)#ip prefix-list Router-to-VGW seq 10 permit 192.168.77.1/32
Apply this prefix list to outgoing BGP advertisements
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#router bgp 65000 (config-router)#address-family ipv4 (config-router-af)#neighbor 169.254.253.17 prefix-list Router-to-VGW out
The IP 169.254.253.17 in this example is the AWS Direct Connect BGP Peer IP.
Confirming that Edge Router and Aviatrix Transit Gateway can Reach each other’s IP for GRE Tunnel
-
In Aviatrix CoPilot, go to Networking > Connectivity > External Connections (S2C) tab.
-
Click + Connection.
-
Enter the following values:
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter a unique name to identify the connection to the external device.
Connect Public Cloud To
-
Select the External Device radio button.
-
Click on the dropdown menu and select BGP over GRE.
Local Gateway
Select the Transit Gateway.
Local ASN
Enter the BGP AS number the Transit Gateway will use to exchange routes with the external device.
Remote ASN
Enter the BGP AS number that the edge router will use to exchange routes with the Transit Gateway.
Over Private Network
Enable this option since AWS Direct Connect is the underlay network.
Learned CIDR Approval
Enable this setting to set up an approval process for gateway learned CIDRs for this BGP external connection. This approval process improves security for your network. If an unapproved CIDR address attempts to access the connection, CoPilot sends an approval email to the CoPilot admin so that the admin can approve or block access.
ActiveMesh Connection
Remote Gateway
Click here to add a remote or on-prem gateway instance.
Remote Gateway Instance IP
Enter the IP address of the remote or on-prem device.
Local Tunnel IP
Leave it blank in this example.
Remote Tunnel IP
Leave it blank in this example.
-
-
Click Connect to generate GRE tunnel and its BGP session.
Downloading the GRE Configuration Sample
-
In CoPilot, go to the Networking* > Connectivity > External Connections (S2C) tab.
-
Find the connection you created and click the vertical ellipsis
 .
. -
Click Download Configuration.
Enter the following values:
Parameter Description Vendor
Select Cisco.
Platform
Select ISR, ASR, or CSR.
Software
Select IOS(XE) for this example.
-
Click Download.
Configuring GRE tunnel on Edge Router
-
Open the downloaded GRE configuration file.
-
Populate these values as follows based on your setup throughout the Tunnel Interface Configuration.
-
<tunnel_number1>: the primary GRE tunnel interface number connecting Aviatrix Transit Primary Gateway (i.e. 11)
-
<tunnel_number2>: the secondary GRE tunnel interface number connecting Aviatrix Transit HA Gateway (i.e. 12)
-
<ios_wan_interface1>: the IP which is assigned on the Loopback interface as an GRE source IP (i.e. 192.168.77.1)
-
<ios_wan_interface2>: the IP which is assigned on the Loopback interface as an GRE source IP (i.e. 192.168.77.1)
-
-
Copy and paste the updated Tunnel Interface Configuration into the edge router.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
interface Tunnel 11 ip address 169.254.61.205 255.255.255.252 ip mtu 1436 ip tcp adjust-mss 1387 tunnel source 192.168.77.1 tunnel destination 10.1.0.185 ip virtual-reassembly no keepalive exit interface Tunnel 12 ip address 169.254.173.77 255.255.255.252 ip mtu 1436 ip tcp adjust-mss 1387 tunnel source 192.168.77.1 tunnel destination 10.1.1.27 ip virtual-reassembly no keepalive exit
Configuring BGP over GRE tunnel on Edge Router
-
Open the downloaded GRE configuration file and copy and paste the BGP Routing Configuration into edge router.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
router bgp 65000 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 169.254.61.206 remote-as 65212 neighbor 169.254.61.206 timers 10 30 30 neighbor 169.254.173.78 remote-as 65212 neighbor 169.254.173.78 timers 10 30 30 ! address-family ipv4 redistribute connected neighbor 169.254.61.206 activate neighbor 169.254.61.206 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor 169.254.173.78 activate neighbor 169.254.173.78 soft-reconfiguration inbound maximum-paths 4 exit-address-family
-
Create a prefix list that defines CIDR where server locates in on-prem/co-location for BGP advertisement.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#ip prefix-list Router-To-Transit-GRE description Advertised on-prem CIDRs 10.220.5.0/24 (config)#ip prefix-list Router-To-Transit-GRE seq 10 permit 10.220.5.0/24
-
Apply the prefix list to outgoing BGP advertisements.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#router bgp 65000 (config-router)#address-family ipv4 (config-router-af)#neighbor 169.254.61.206 prefix-list Router-To-Transit-GRE out (config-router-af)#neighbor 169.254.173.78 prefix-list Router-To-Transit-GRE out
Verifying GRE Tunnel Status on Aviatrix Controller
-
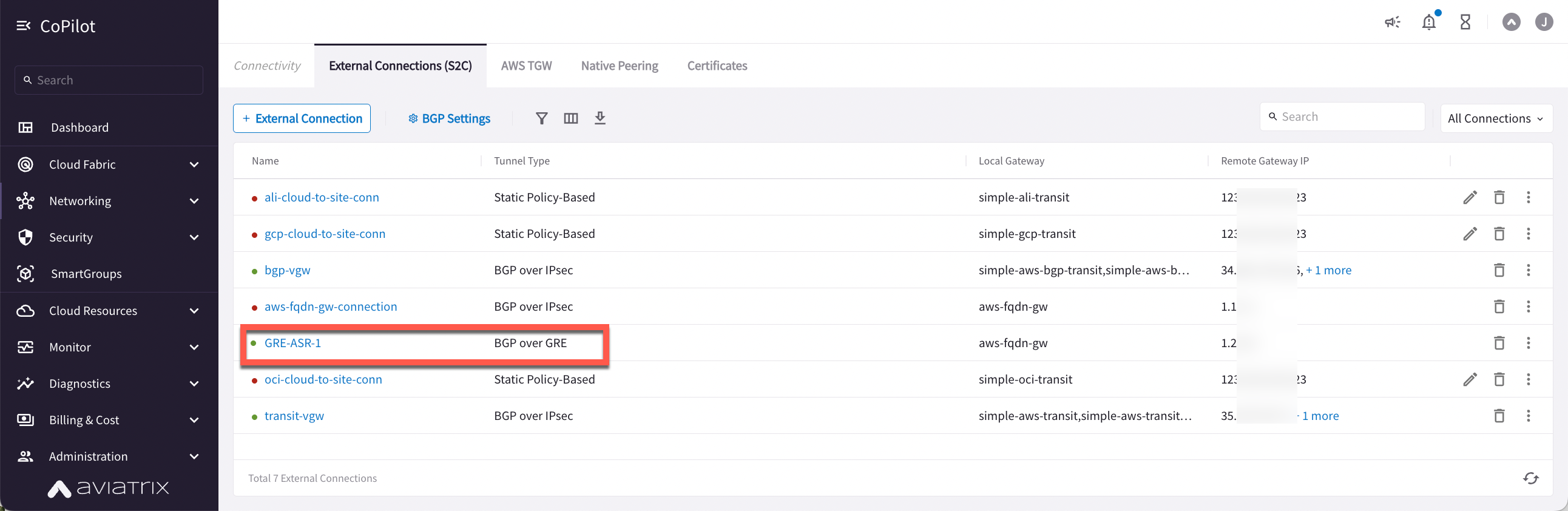
In CoPilot, go to Networking > Connectivity > External Connections (S2C) tab.
-
Find the connection that you created. The green dot next to the Connection Name indicates the connection is Up.
-
Go to Cloud Fabric > Gateways > Transit Gateways.
-
Select the Transit Primary Gateway that was created in the previous step.
-
Click Details/Diag.
-
Click the Connections sub-tab.
-
Find the connection that you created with Connection Name in the previous step and check the Tunnel Status.
Verifying BGP Session Status
-
Go to Diagnostics > Cloud Routes > BGP Info.
-
Find the connection that you created with Connection Name in the previous step and check the status. The Status should be Established. If some external connections for the selected Transit Gateway are Not Established, the overall BGP Status for the Transit Gateway is Partially Established.
Configuring ECMP Load Balancing for High Performance
Building Multiple GRE tunnels between Edge Router and Aviatrix Transit Gateway
-
Building multiple GRE tunnels by repeating Build connectivity between edge router and Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Build multiple BGP over GRE tunnels by repeating Build GRE tunnel and BGP over GRE.
In this example, we build up to 4 pairs of GRE connections (total up to 8 tunnels) to benchmark performance.
Enabling BGP ECMP feature on Aviatrix Transit Gateway
-
In CoPilot, go to Cloud Fabric > Gateways > Transit Gateways and select the Transit Gateway that was created in the previous step.
-
On the Settings sub-tab, under Border Gateway Protocol, toggle the BGP ECMP setting to On.
Verifying BGP ECMP feature on Aviatrix Controller
-
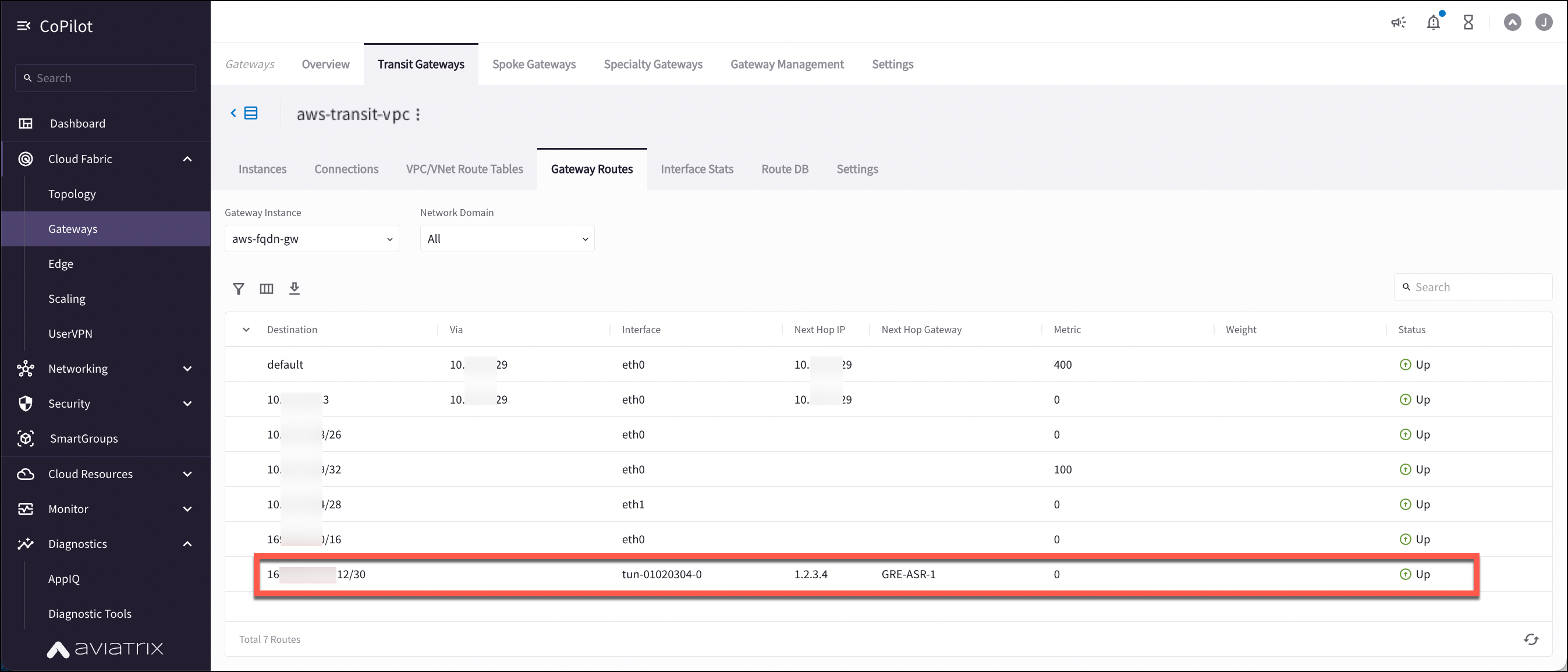
With the same Transit Gateway selected, click the VPC/VNet Route Tables tab.
-
Select the Transit Primary Gateway that was created in the previous step.
-
Click the Gateway Routes sub-tab.
-
Search for the on-prem CIDR in the Destination column.
-
Check whether there are multiple GRE tunnels with same Metric and Weight under the same route entry.
Enabling the BGP ECMP feature on Edge Router
Configure "maximum-paths" with higher number of equal-cost routes in BGP settings so that BGP will install in the routing table. In this example, we configure "maximum-paths 8" to achieve high performance over multiple GRE tunnels.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#router bgp 65000 (config-router)#address-family ipv4 (config-router-af)#maximum-paths 8
-
Modify ECMP Load Balancing algorithm depending on traffic type.
Simple Cisco IOS example:
#configure t (config)#ip cef load-sharing algorithm include-ports source destination
Ready to Go
At this point, run connectivity and performance test to ensure everything is working correctly.