Transit Multi-Peer BGP over LAN in GCP Workflow
Introduction
Transit BGP to LAN allows Aviatrix Transit Gateways to communicate with multiple instances in the same VPC in GCP without running any tunneling protocol such as IPsec or GRE (traffic needs to be sent to the subnet gateway for forwarding). One use case is to interoperate with third-party virtual appliances such as SD-WAN cloud instances that do not have the capability to support BGP over any tunneling protocols.
For example, integrating with SD-WAN gateways can be deployed as below, where Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Gateways connect to third-party cloud instances in the same VPC in GCP:
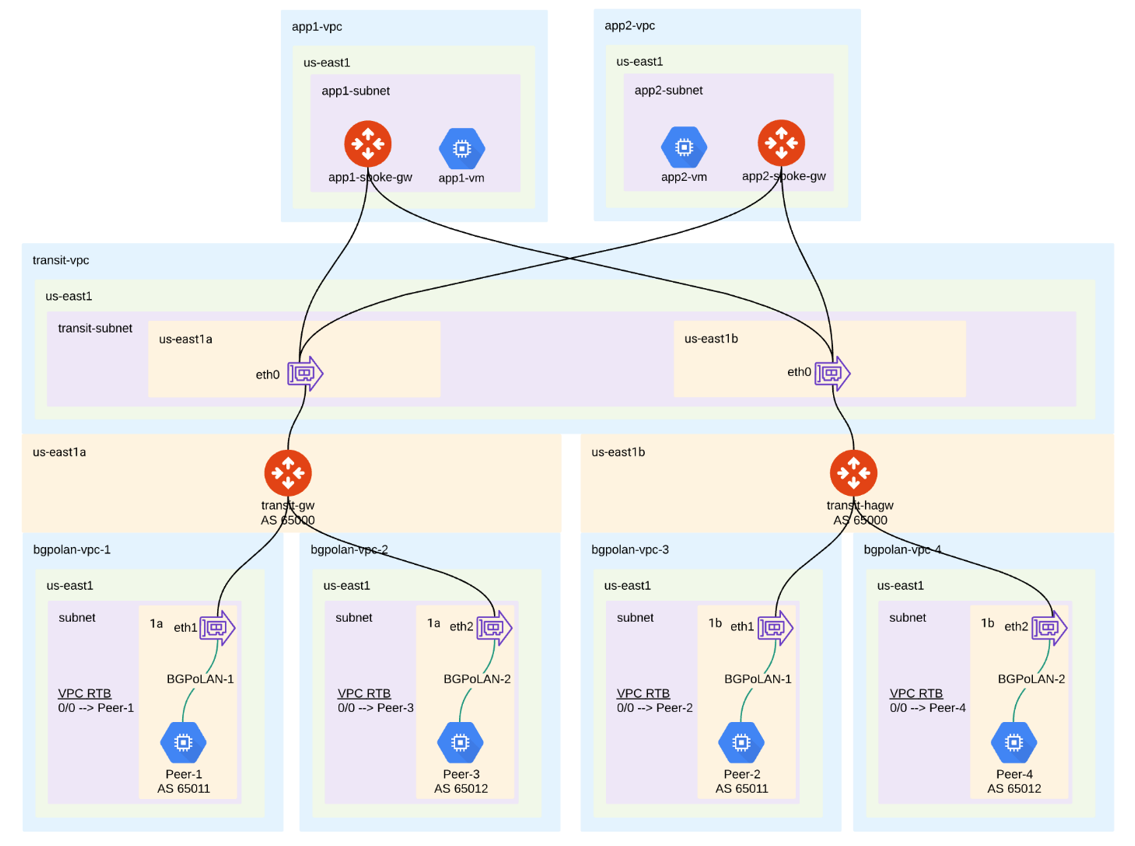
This document describes a step-by-step instruction on how to build Aviatrix Transit Gateway to External Device using BGP over LAN. In this Tech Note, you will learn the following:
For other BGP over LAN workflows, see:
For more information about Multicloud Transit Network and External Device, see:
|
The key ideas for this solution are:
-
A BGP session establishes between third-party cloud instances and Aviatrix Transit Gateways via each LAN interface in the same VPC.
-
Dataplane traffic also runs between third-party cloud instances and Aviatrix Transit Gateways via each LAN interface without a tunnel protocol such as IPsec or GRE.
Prerequisites
-
Upgrade Aviatrix Controller to at least version 6.6.
-
Third-party cloud instance supports high throughput.
Deploying Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Solution
Refer to Global Transit Network Workflow Instructions for the below steps. Please adjust the topology depending on your requirements.
-
Deploy Aviatrix Multicloud Transit Gateway and HA with High Performance Encryption Mode encryption enabled in Transit VPC. Ensure that you create the required number of BGP over LAN connections.
-
Deploy Spoke Gateway and HA with High Performance Encryption Mode encryption enabled in Spoke VPC(s).
Launching Third-Party Cloud Instances
Deploy third-party cloud instances with an interface in the same VPC as the Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Create a third-party cloud instance and put the MGMT interface in public gateway subnet.
-
Create a new WAN subnet and dedicated routing table for the WAN interface if needed.
-
Create a new LAN subnet and a dedicated routing table for the LAN interface.
-
Make sure the IP forwarding function is enabled on the third-party cloud instances.
|
GCP allows a maximum of eight interfaces per instance, and the maximum limit depends on the number of vCPUs. Due to this limitation, the solution supports seven BGP peers without FireNet enabled and six BGP peers with FireNet enabled. |
Building BGP over LAN
-
In CoPilot, navigate to Networking > Connectivity > External Connections (S2C).
-
Click +External Connection.
-
In the Add External Connection dialog, select Connect Public Cloud to External Device.
-
Select BGP over LAN from the drop-down.
-
Enter the following information in the fields provided.
Setting Value Name
Unique name to identify the external device connection.
Local Gateway
Select the Transit VPC ID where the Transit gateway was launched (BGP over LAN must have been enabled for this Transit gateway).
Local ASN
The local BGP AS number (for on-site equipment) the Spoke gateway will use to exchange routes with the external device.
Remote ASN
Enter the BGP AS number of the cloud location the external device will use to exchange routes with the Transit Gateway.
BGP ActiveMesh
Enable full mesh BGP connections to the external devices.
Learned CIDR Approval
Set to On by default if selected for the Local Gateway. Otherwise, it is set to Off.
Remote LAN IP
The private IP of the LAN interface of the third-party cloud primary instance.
Local LAN IP
Aviatrix detects the Local LAN IP automatically and assigns an IP in the same subnet as the Remote LAN IP. Optionally, you can configure a specific IP within the same subnet as the Remote LAN IP.
-
Click Connect to generate the BGP sessions.
-
Create an external connection for each BGP peer.
(Optional) Downloading the BGP over LAN configuration sample from Aviatrix Controller
-
On the External Connections (S2C) tab, click the vertical ellipsis
 and then select Download Configuration.
and then select Download Configuration. -
In the Download Configuration dialog, select the following:
-
Vendor: select the device you are using (any device that is capable of running IPsec and BGP).
-
Platform: select the applicable platform for the chosen device.
-
Software: automatically selected based on the Vendor/Platform you select.
-
-
Click Download.
Configuring BGP over LAN on the Third-Party Cloud Instance(s)
-
(Optional) Open the downloaded BGP over LAN configuration file.
-
Configure the relevant BGP over LAN information on the third-party cloud instance(s).
Verifying the Connection Status
Navigate to Diagnostics > Cloud Routes > Gateway Routes to check the gateway and tunnel status.
Verifying the BGP session status on Aviatrix Controller
Navigate to Diagnostics > Cloud Routes > BGP Info and expand a Gateway Name to check the Neighbor Status. The Status should be Established. If some external connections for the selected Transit Gateway are Not Established, the overall BGP Status for the Transit Gateway is Partially Established.
Ready to Go
At this point, run connectivity and performance tests to ensure everything is working correctly. You can use the Diagnostic Tools for this.