About Aviatrix Edge Gateway High Availability
This document provides an overview of the Aviatrix Secure Edge High Availability feature.
Before reading this document, you should be familiar with the following:
About Highly Available Edge Gateway Configuration
The Aviatrix Secure Edge High Availability feature supports active-active and active-standby peering connections to the Transit Gateway for high availability and scalability.
Active-Standby Edge
Highly Available (Active-Standby Mode) - This type of deployment provides highly available Edge Gateways without scalability. In an active-standby configuration, an Edge site can consist of only two Edge Gateways, primary (active) and secondary (standby). The primary and the secondary Edge Gateways connect to the Transit Gateway with one active peering and one standby peering. Only the primary Edge Gateway actively forwards network traffic. The secondary Edge Gateway takes over when the primary gateway is down.
If you select Active-Standby mode, you can also set Preemptive mode to determine the network’s behavior when the primary gateway is back up again.
-
When Preemptive is On, the network automatically switches back to using the primary gateway when the gateway connection is back up.
-
When Preemptive is Off (which is the default), the network continues to use the secondary gateway even after the primary gateway is back up.
Active-Active Edge
Highly Available (Active-Active Mode) - This type of deployment provides highly available Edge Gateways with scalability. In an active-active configuration, an Edge site can consist of multiple Edge Gateways. You can create multiple gateways to scale your Edge Gateways for throughput. Gateway scaling provides the flexibility to add or remove gateways to handle workloads at different peak times to ensure high availability and improve and maintain network stability and performance. In an active-active configuration, all the gateways are in active-active mode and connect to the Transit Gateway with active peering connections. Network traffic between the Transit and Edge Gateways is load balanced and forwarded across all active peering connections by using Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP) routing.
| Edge Gateway scalability is supported only with the latest version of the Aviatrix Controller. |
About Creating Highly Available Edge Gateways
Aviatrix Edge Gateways are associated with an edge site. When you create an Edge Gateway for an edge site, you have the option to enable High Availability (HA) mode.
Aviatrix Secure Edge supports Active-Active and Active-Standby high availability modes for peering connections to the Aviatrix Transit Gateway. When Edge Gateway High Availability is enabled, a second HA Edge Gateway is created.
|
This example shows an active-standby Edge deployment with two gateways (one primary and one HA Edge Gateway) for the same edge site for high availability.
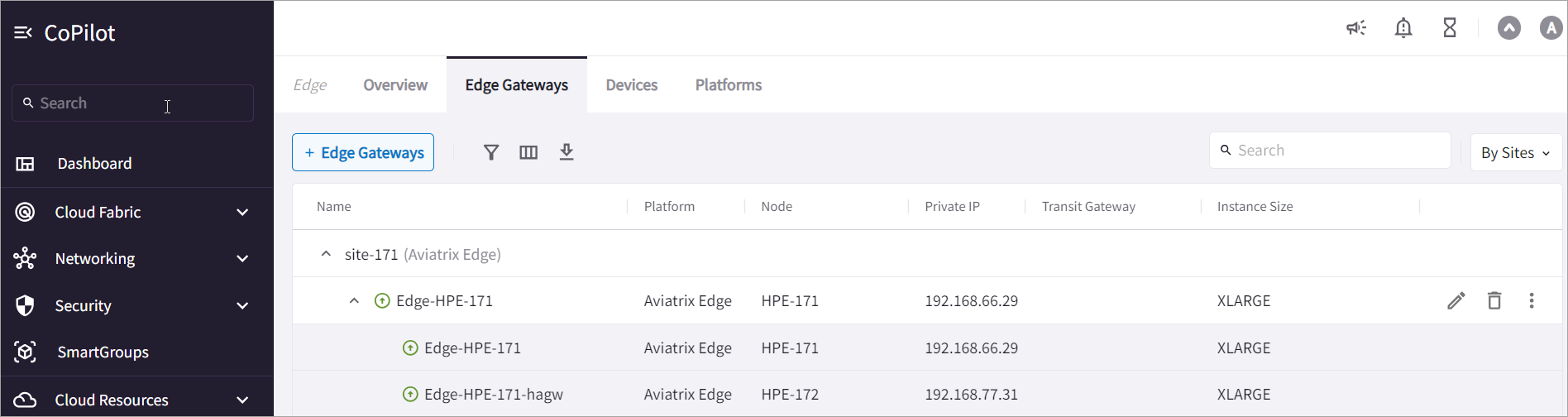
CoPilot auto-generates the name of the HA gateway in the format <_primary-gateway-name_>-<_hagw_>.
The example below shows an active-active Edge deployment with multiple Edge Gateways for the same edge site for scalability. A maximum of eight Edge Gateways are supported per site.
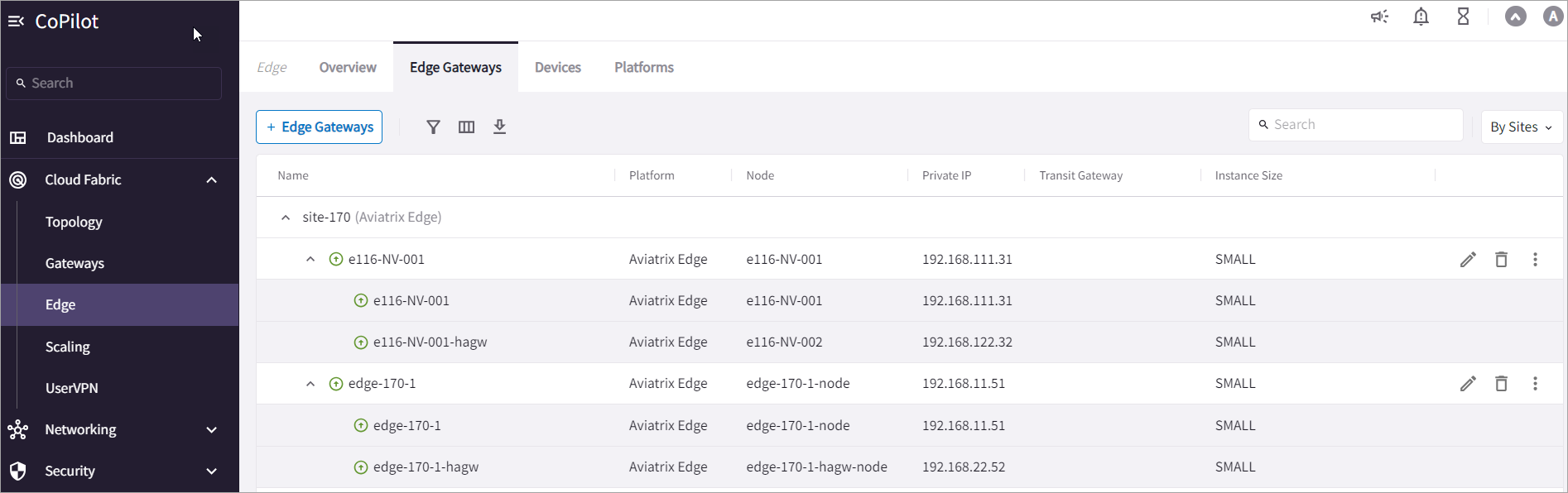
Network traffic flow is load balanced to all the gateways by using Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP) routing.
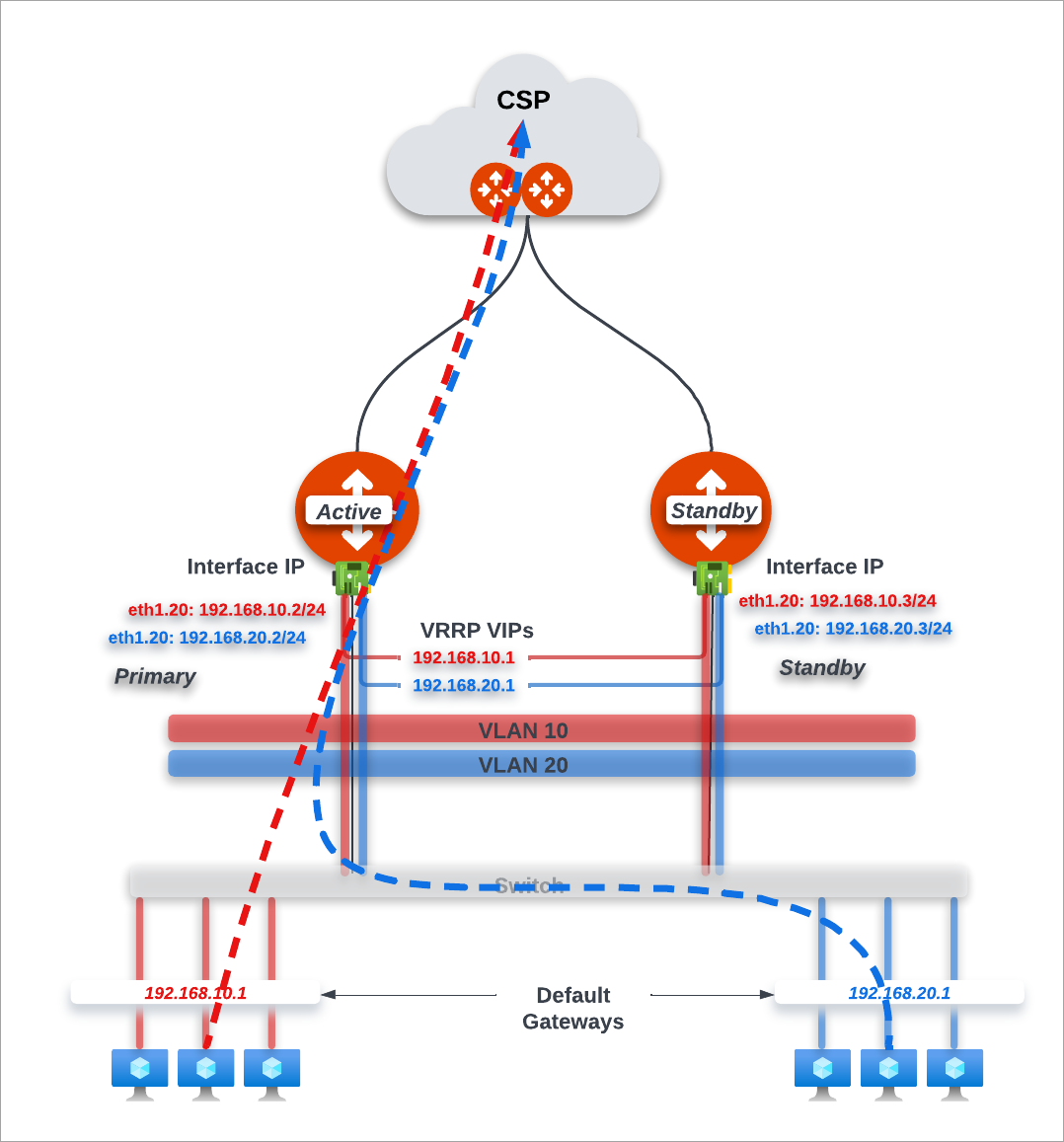
About Edge Gateway with VRRP Configuration
An Edge Gateway can be deployed in on-premises locations as the default LAN router supporting Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) protocol.
| Edge Gateway with VRRP support requires the primary and secondary Edge Gateways to be created in Active-Active High Availability mode. |
The diagram below illustrates an Edge Gateway with VRRP Active-Standby configuration. LAN traffic flows to the VRRP Active gateway to the cloud. When the VRRP Active gateway is down, traffic flows to the VRRP standby gateway to cloud.