Configuring Azure Multi-Peer BGP over LAN with Azure Route Server Integration
Introduction
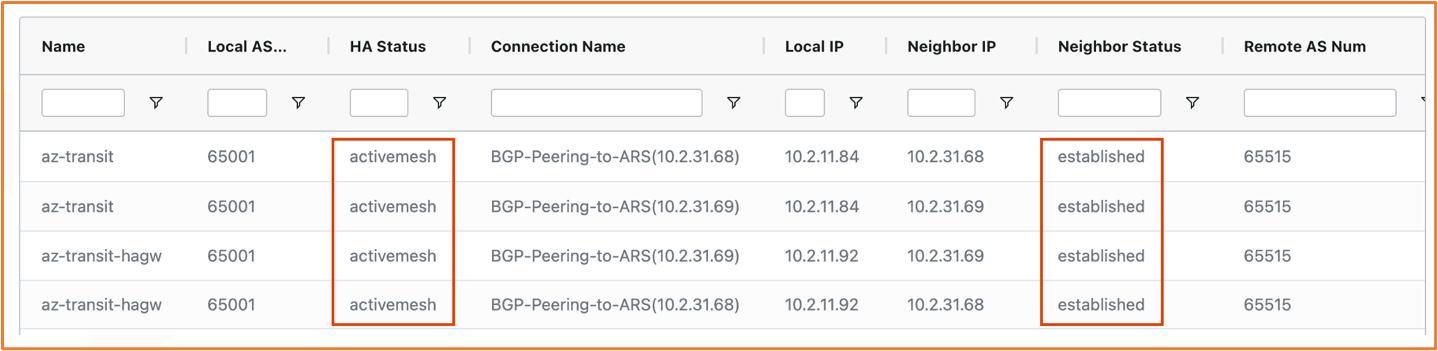
The Aviatrix Controller allows Azure Route Server (ARS) integration for on-premises connectivity using Azure ExpressRoute with no overlay. Azure Route Server is a managed service that is highly available. It provides a mechanism for exchanging routes between Azure Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs) dynamically through Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). You can achieve full-mesh high availability by running two BGP peering endpoints.
Aviatrix integrates with Azure Route Server by treating the Azure Route Server as a BGP over LAN peer and exchanging routes using BGP. This enables Azure cloud networks to connect to on-prem or branch locations and provides connectivity across hybrid environments. Customers who use high-speed Azure ExpressRoute connectivity with no encryption for hybrid environments can exchange routes between the Aviatrix Transit Gateways and the on-prem network connected via ExpressRoute. This solution provides you with an enterprise-grade transit network.
The diagram below shows Azure Route Server integration with Aviatrix Transit Gateways. Full mesh is enabled so that both Transit Gateways peer with the two Azure Route Server IP endpoints in the Azure Route Server.
Prerequisites
-
Aviatrix Controller is updated to software version 6.8 or above.
-
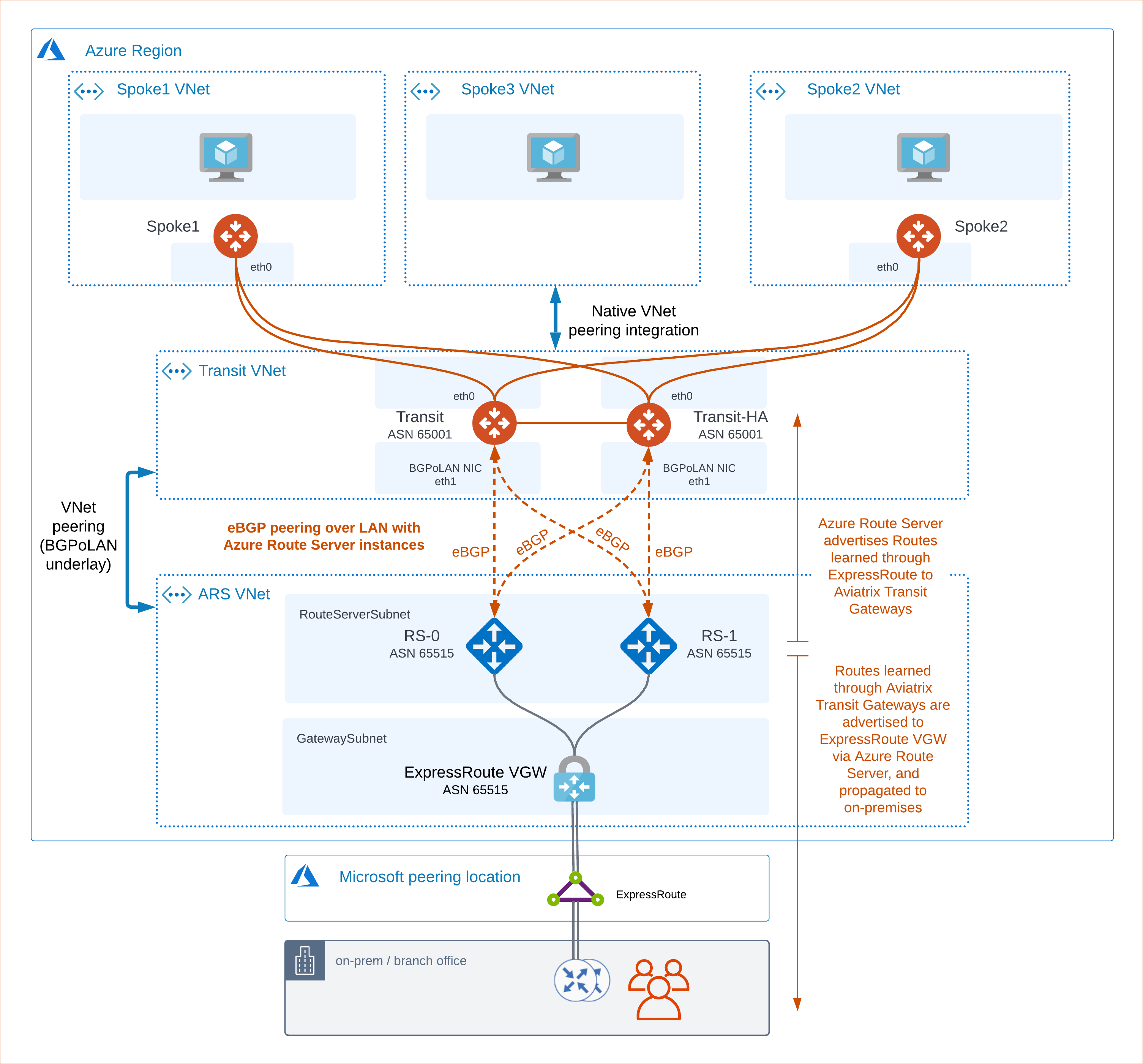
Aviatrix Transit Gateways are deployed with Insane Mode (mandatory) and with BGP over LAN enabled. You only need to configure one BGP over LAN interface to peer with both Azure Route Server instances.
-
A BGP ASN is assigned to the Transit Gateways (configured on the Aviatrix Controller in Multi-Cloud Transit > Advanced Config > Local AS Number).
Complete the following tasks in Azure:
-
Create a VNet to deploy the Azure Route Server.
-
Deploy the Azure Route Server in this VNet by referring to the applicable Azure documentation.
-
Go to your Route Server > Overview and record the ASN and the private IP addresses of the Azure Route Server endpoints you created. You will use these later in the Aviatrix Controller configuration.

Configure VNet Peering Between Transit VNet and Azure Route Server
You need to configure the VNet peering between the VNet that is hosting the Azure Route Server and the Aviatrix Transit VNet. Follow these steps to configure the peering parameters from the Azure Route Server VNet to the Aviatrix Transit VNet.
| If you are using Terraform, make sure to explicitly set the argument “allow_forwarded_traffic” to “True” for both VNet peerings. |
-
Launch the Azure Portal.
-
Go to Virtual networks and select your Route Server VNet.
-
Under Settings, click Peerings.
-
On the Peerings page, click Add.
-
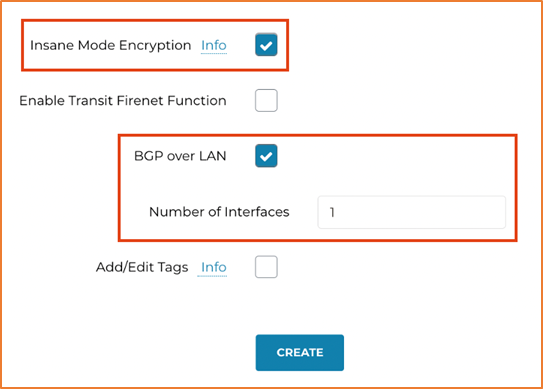
On the Add peering page, select the following options:
-
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
Traffic to remote virtual network |
Allow |
Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network |
Allow |
Virtual network gateway or route server |
Select the appropriate Azure account |
-
Go to Virtual networks and select your peered Transit Server VNet.
-
Under Settings, click Peerings.
-
On the Peerings page, click Add.
-
On the Add peering page, select the following options:
-
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
Traffic to remote virtual network |
Allow |
Traffic forwarded from remote virtual network |
Allow |
Virtual network gateway or route server |
Select Use the remote virtual network gateway or route server |
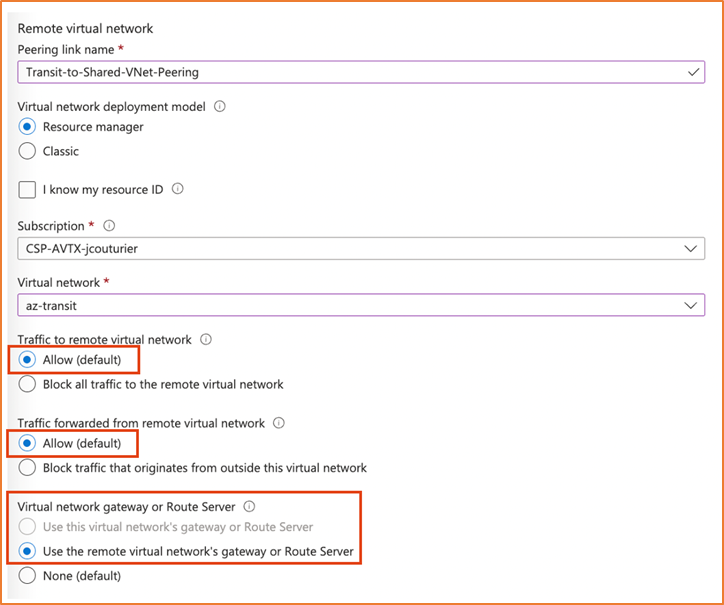
-
Click Add.
Configure BGP peering Between Azure Route Server and Transit Gateways
-
In your Aviatrix Controller, go to Multi-cloud Transit > List, select your primary Transit gateway and click Details/Diag.
-
Click on Gateway Interface Info and record the IP address assigned to the BGP over LAN interface of both the primary and HA Transit gateways.
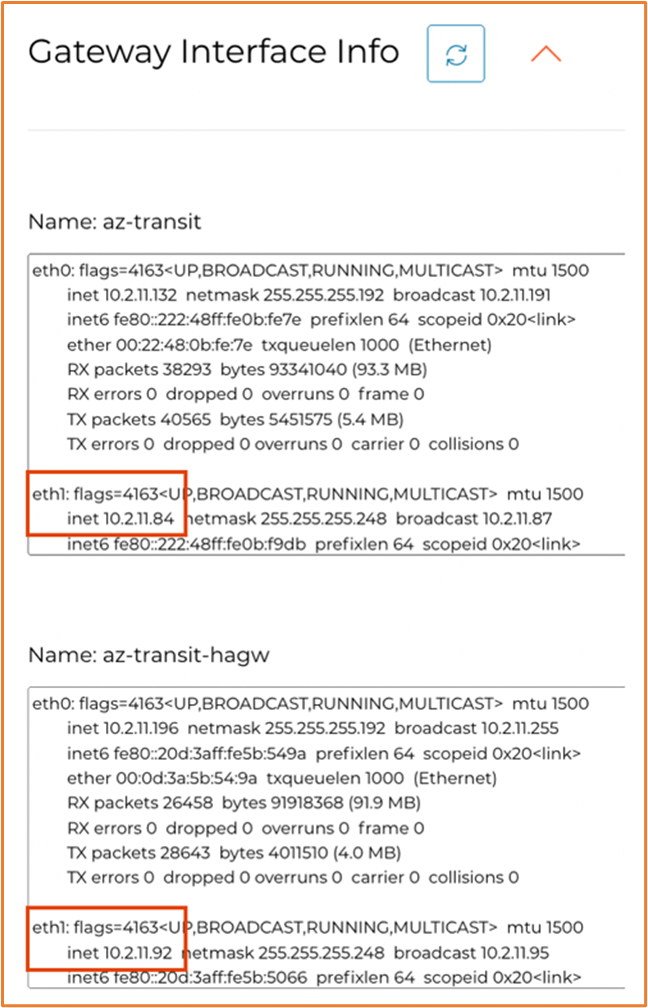
-
In your Azure portal, go to Route Servers > select your Azure Route Server > Peers. Click Add and configure the Azure Route Server peering to both remote Aviatrix Transit Gateways in the Transit VNet by specifying the ASN you configured for your Aviatrix Transit Gateways and the IP address of the BGP over LAN network interface on each Transit Gateway. See the Prerequisites section to find the ASN number.

-
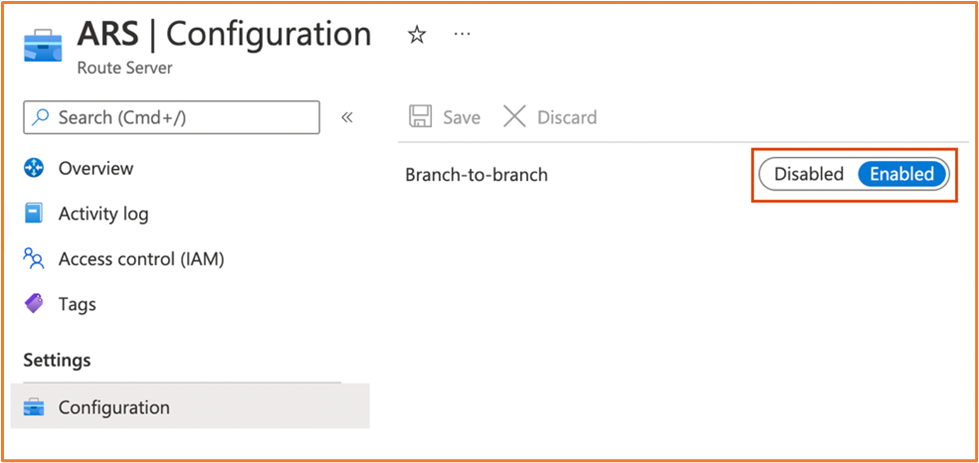
Go to Route Servers > select your Azure Route Server > Configuration.
-
Next to Branch-to-branch, select Enabled. This option allows the Azure Virtual Network Gateways to propagate the routes the Azure Route Server has learned from the Aviatrix Transit Gateways. It is disabled by default.
Configure External Connection in Controller
-
Open the Aviatrix Controller.
-
Go to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup > External Connection.
-
In Connect to VGW / External Device / Azure VNG, select the following options:
-
External Device
-
BGP
-
LAN
-
-
Use the VPC Name / Site ID drop-down menu to select the Transit Gateway.
-
Mark the checkbox for Enable Remote Gateway HA.
-
Mark the checkbox to enable BGP Activemesh.
| The BGP Activemesh option is only available when you select a Transit Gateway in VPC Name / Site ID. |
When you select BGP Activemesh, Aviatrix Controller creates two peers from each Transit Gateway to both instances of Azure Route Server. This is required for the correct operation of Azure Route Server.
-
In the remaining fields, enter the ARS IP addresses. Use the IP addresses for each Azure Route Server instance as reported in the Azure portal.
| Azure Route Server always resides in ASN 65515 and cannot be changed. |
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
Remote BGP AS Number |
65515 |
Remote vnet:rg:sub |
ARS VNET |
Remote LAN IP |
ARS instance 0 IP address. See Prerequisites above for where to find the Azure Route Server IP addresses. |
Local LAN IP |
Primary Transit Gateway BGPoLAN IP address. The BGPoLAN address of the gateway is suggested automatically. |
Remote BGP AS number (Backup) |
65515 |
Remote LAN IP (Backup) |
ARS instance 1 IP address |
Local LAN IP (Backup) |
HA Transit Gateway BGPoLAN interface IP address |
|
To confirm that the Aviatrix Controller set up the Azure Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) peering in Steps 5 and 6, go to Multi-Cloud Transit > BGP > Connections. You may need to use the sorting tool in the Remote AS Num column to identify the pairs of Route Servers. In the HA Status column, confirm that Activemesh is the status for the Route Servers and confirm that Neighbor Status is established. You can also use CoPilot to check the status of the BGP peerings to the Azure Route Server and the BGP routes learned/advertised. In CoPilot, go to Cloud Routes > BGP Info and click on the BGP Map, Learned Routes, or Advertised Routes button to get more details. |