Azure Ingress Firewall Setup Solution
Azure Ingress Traffic Inspection Firewall
This document illustrates a simple architecture for Ingress traffic inspection firewall that leverages Azure Load Balancers, Transit FireNet, and Azure Transit with Native Spoke VNets. The solution also allows you to view the client IP address.
The deployment is shown in the below diagram.
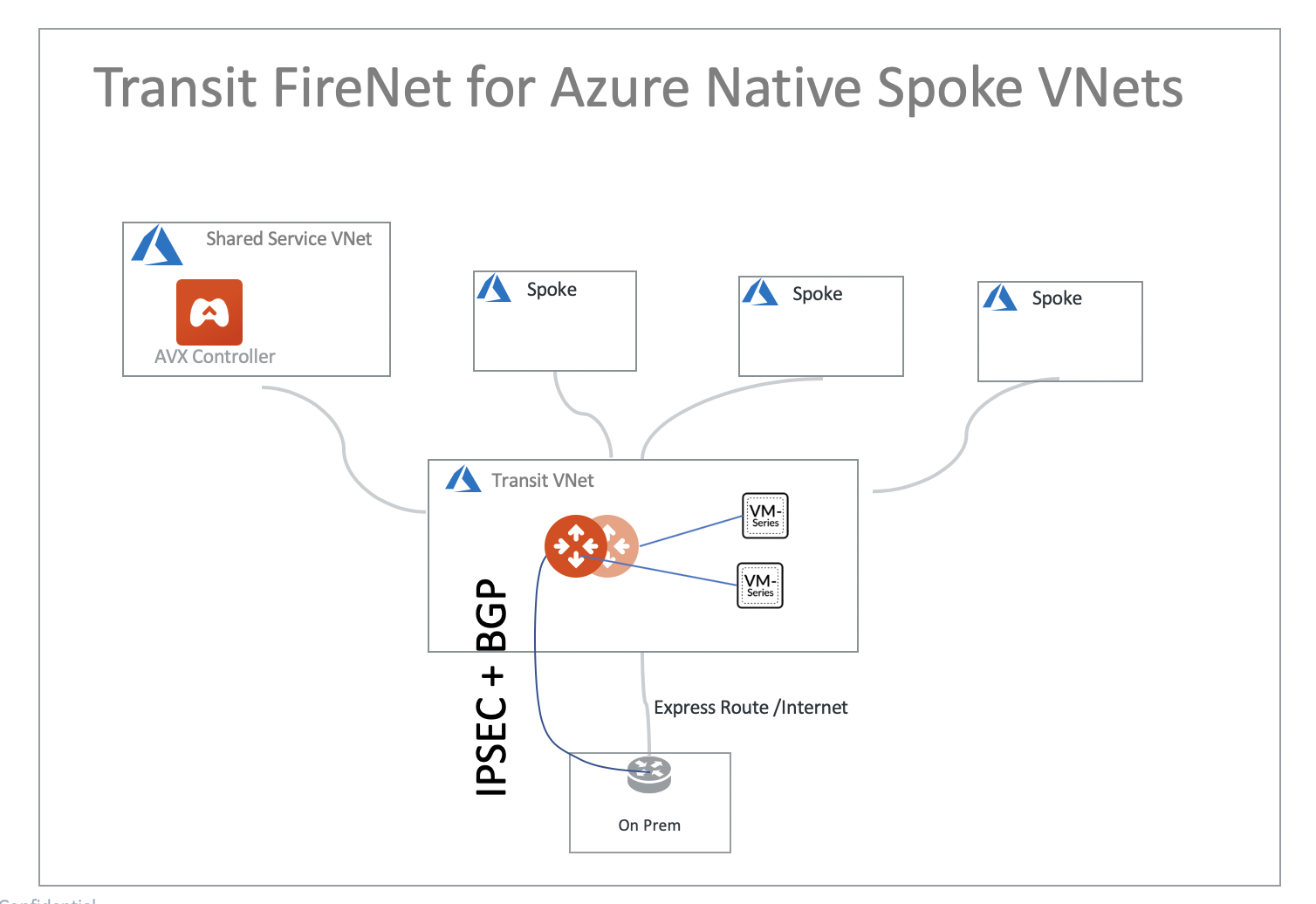
The key idea is that from a FireNet point of view, the ingress inspection is simply a VNet-to-VNet traffic inspection. This is accomplished by:
-
Placing an Internet facing Azure Application Gateway in a Spoke VNet (in the diagram, this spoke VNet is called Ingress Spoke VNet) to load balance traffic to the VNet where applications reside (Application Spoke VNet).
-
Managing Spoke Inspection Policies for the Application Spoke VNet traffic that requires inspection with the Aviatrix Transit VNet.
In this unified architecture, firewalls can be used for Ingress, Egress, North-South and VNet-to-VNet filtering. The solution does not need Azure Load Balancers to directly attach to firewall instances which then requires firewall instances to source NAT the incoming traffic from the Internet. Firewall instances can scale out as applications scale for all traffic types.
|
This architecture works for Azure Application Gateway. You can create multiple load balancers in the Ingress Spoke VNet. |
Prerequisite Setup for Azure Ingress Firewall Setup Solution
First, upgrade the Aviatrix Controller to at least version UserConnect-5.3.1428.
Deploy the below topology in Azure:
-
Azure VNets
-
Aviatrix Transit VNet (i.e. 192.168.23.0/24)
-
Ingress Spoke VNet (i.e. 10.20.0.0/16)
-
Application Spoke VNet (i.e. 10.21.0.0/16)
-
-
Azure Transit with Native Spoke VNets topology
|
Aviatrix Transit FireNet for Azure Encrypted Transit topology also supports this Azure Ingress Firewall Solution. |
Deploy an Aviatrix Transit VNET for the Azure Ingress Firewall Setup Solution
Create an Aviatrix Transit VNet with the Aviatrix FireNet VPC option enabled.
-
In CoPilot, go to Cloud Resources > Cloud Assets > VPC/VNets and Subnets.
-
Click + VPC/Vnet and create a new VPC with the Azure ARM Cloud Type.
-
From the VPC Function drop-down select Transit + FireNet.
-
Click Save.
Deploying an Ingress Spoke VNET
Create an Ingress Spoke VNET by creating a VNet as per Deploy an Aviatrix Transit VNet. You can also use an existing VNet.
Deploying an Application Spoke VNET for the Azure Ingress Firewall Setup Solution
Create an Application Spoke VNET as per the previous step or manually deploy it in the Azure portal. You can also use your existing Application VNET.
Deploying Azure Transit with Native Spoke VNets Topology
Follow Global Transit Network Workflow Instructions (AWS/Azure/GCP/OCI) to deploy Azure Transit with Native Spoke VNets topology.
Create an Aviatrix Transit Gateway in Aviatrix Transit VNET by following the Launch a Transit Gateway procedure.
|
For Azure deployment, the Aviatrix Transit Gateway must be launched with the option Enable Transit FireNet Function enabled. The minimum Azure FireNet gateway size is Standard_B2ms. |
Managing Transit FireNet Policy for Azure Ingress Firewall Setup Solution
-
Follow Aviatrix Transit FireNet creation to deploy FireNets.
-
Launch firewall instances here.
-
Manage a spoke inspection policy for the Application Spoke VNET by referring to Configuring FireNet Connection Policies.
Here is the Firewall information in this example for your reference. Adjust it depending on your requirements.
| Example setting | Example value |
|---|---|
Firewall Image |
Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Next-Generation Firewall Bundle 1 |
Firewall Image Version |
9.1.0 |
Firewall Instance Size |
Standard_D3_v2 |
Management Interface Subnet |
Select the subnet whose name contains "gateway-and-firewall-mgmt" |
Egress Interface Subnet |
Select the subnet whose name contains "FW-ingress-egress" |
Username |
Applicable to Azure deployment only. “admin” as a username is not accepted. |
Attach |
Check |
-
Set up firewall configuration by referring to Example Config for Palo Alto Network VM-Series.
In Azure, instead of using the pem file, use username/password to ssh into firewall instance to reset the password if needed. Additionally, use the same username/password to login into the firewall UI.
Launching an Apache2 Web server in Application Spoke VNET
In Application Spoke VNET, create an Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS virtual machine and install Apache2 HTTP Server with custom port 8080.
| Example Setting | Example Value |
|---|---|
Protocol |
HTTP |
Port |
8080 |
|
Refer to Install The Latest Apache2 HTTP Server ( 2.4.34 ) On Ubuntu 16.04 | 17.10 | 18.04 LTS Servers to install Apache2 HTTP Server. Refer to How To Change Apache Default Port To A Custom Port to use custom port 8080. |
Creating Azure Application Gateway
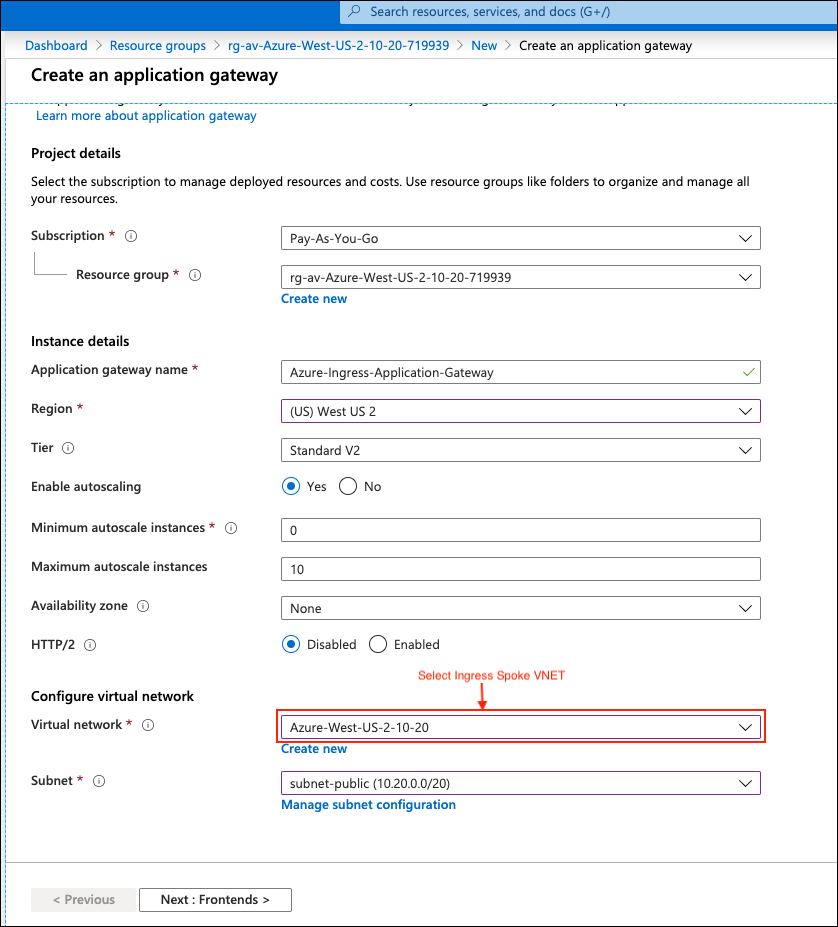
In Ingress Spoke VNET, create an Azure Application Gateway. Make sure you select the following:
-
Create an Azure Application Gateway in Ingress Spoke VNET.
-
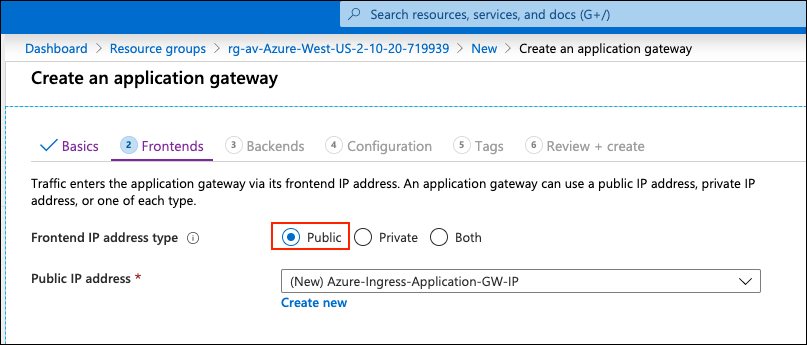
Under Frontends, select Public for the Frontend IP address type.
-
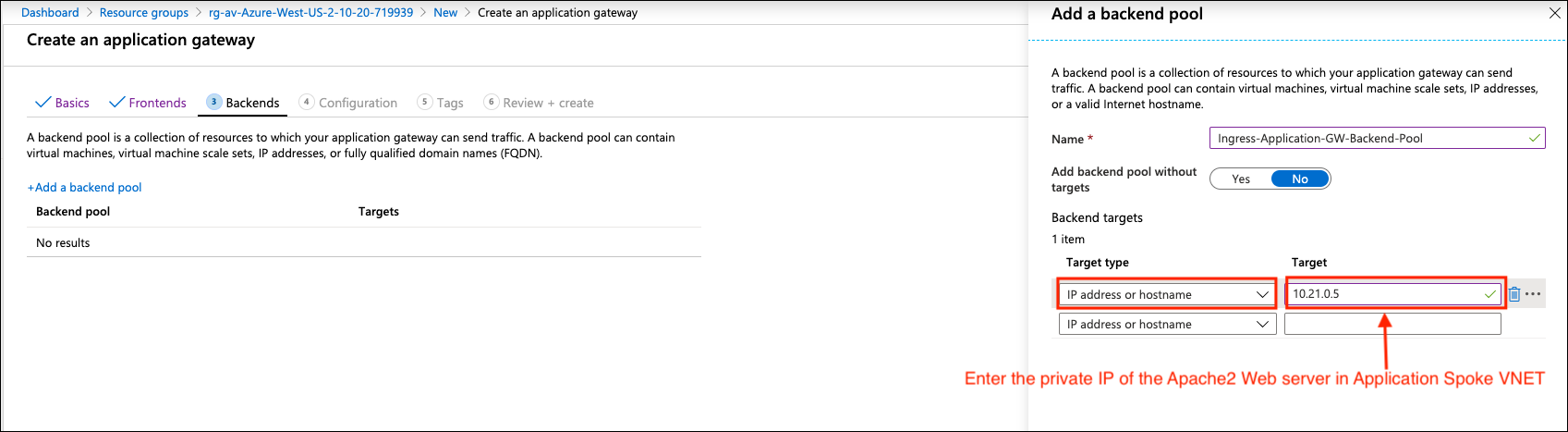
Select IP address or hostname for Target type and configure the private IP of Apache2 Web Server for Target in section Backends.
-
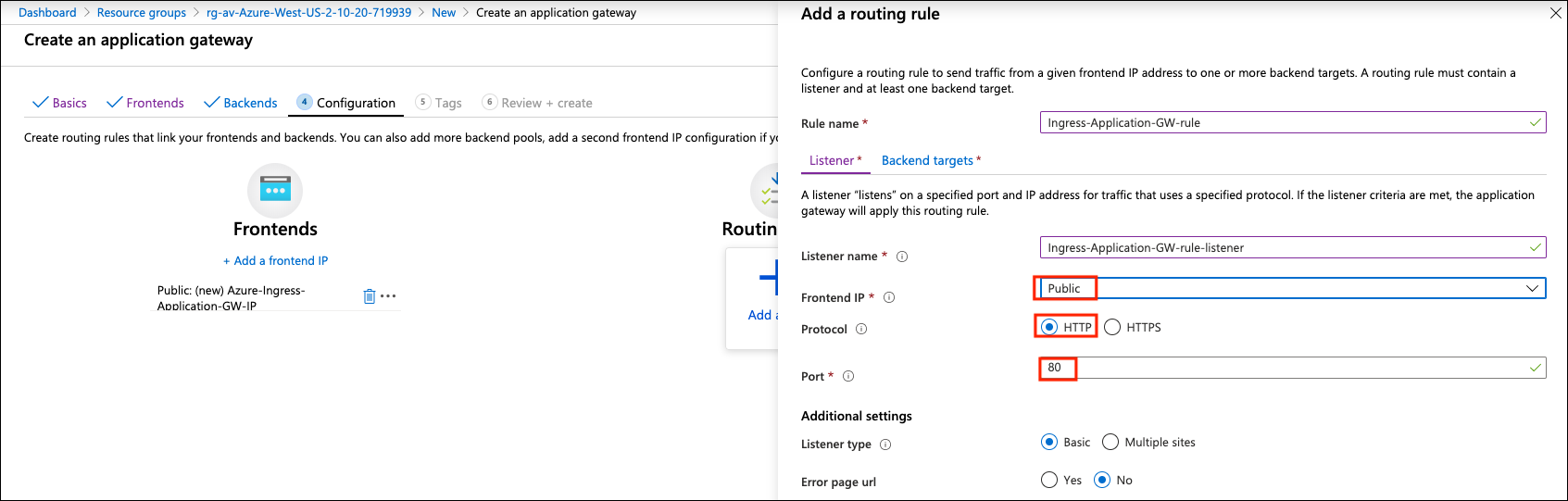
Add a routing rule on the Listener depending on your requirements.
Example setting Example value Frontend IP
Public
Protocol
HTTP
Port
80
-
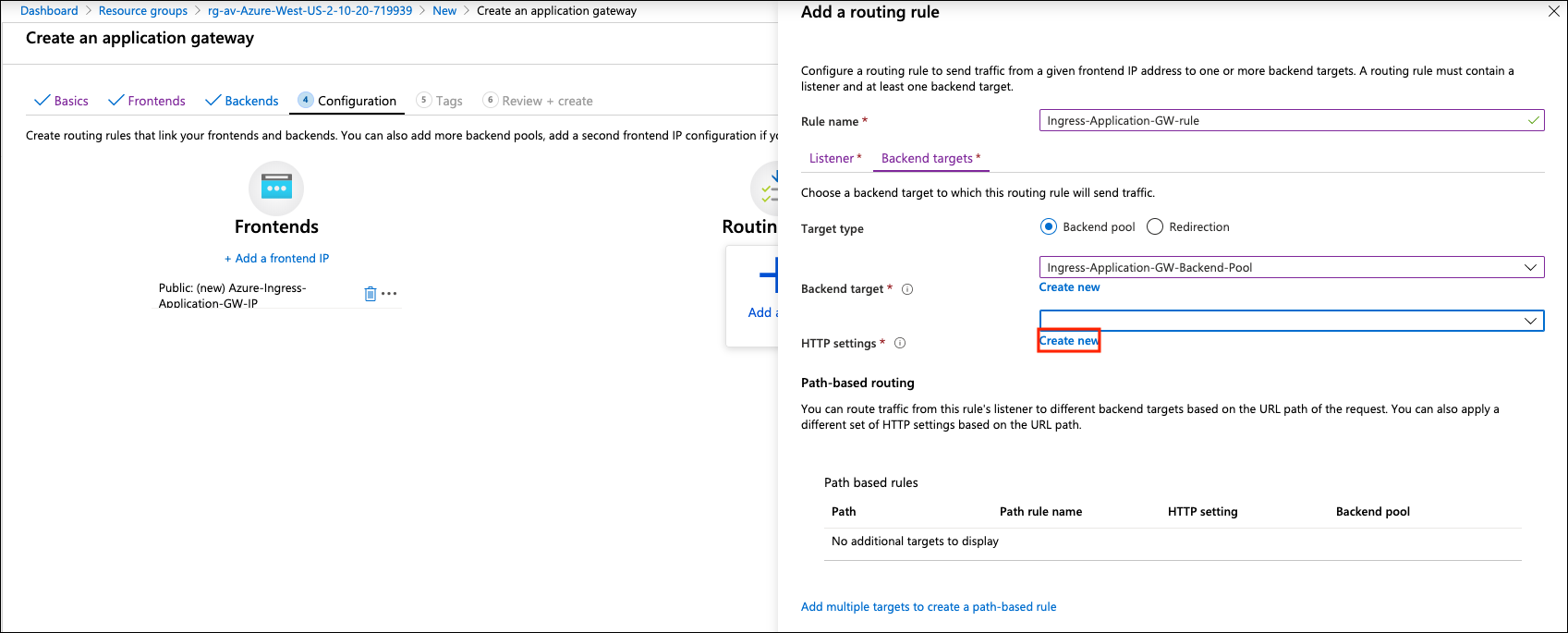
Add a routing rule on Backend targets and create an HTTP setting depending on your requirement.
-
Click Create new on HTTP settings.
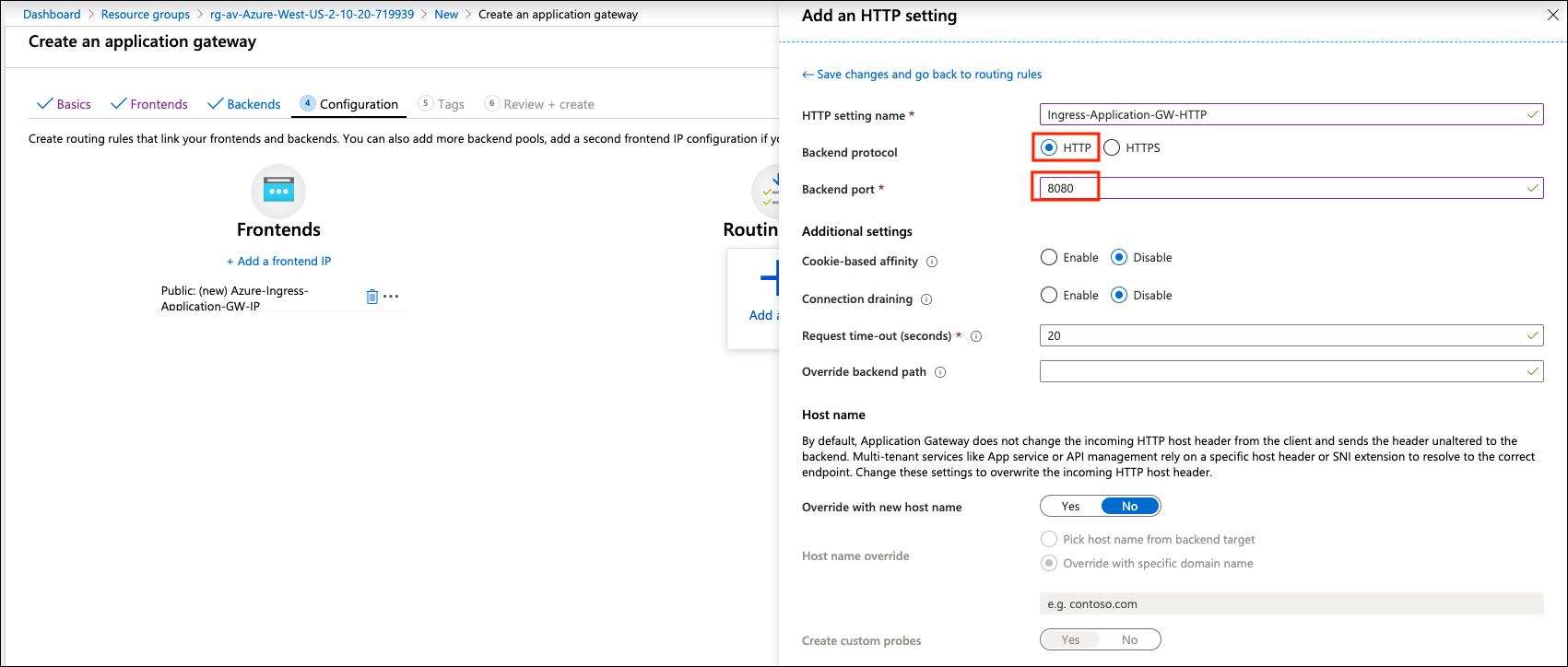
| Example Setting | Example Value |
|---|---|
Backend protocol |
HTTP |
Backend port |
8080 |
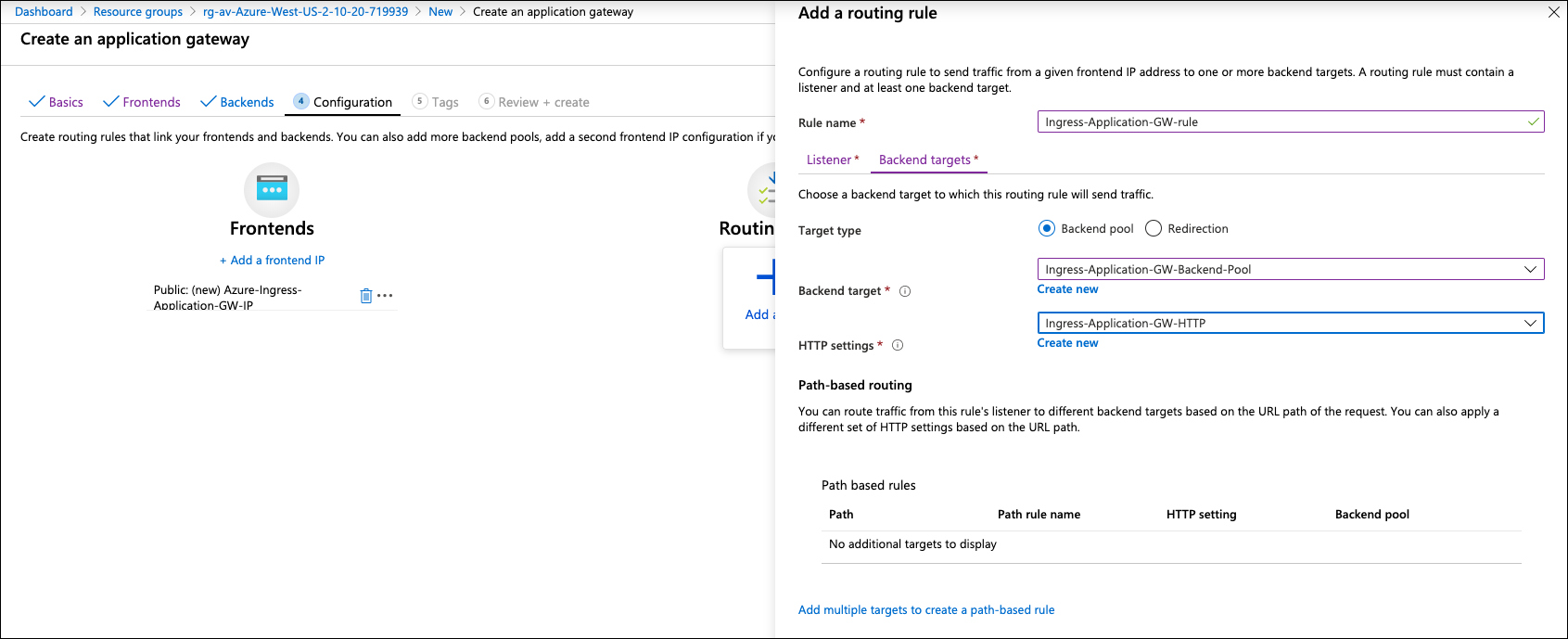
-
Review the configuration and click Create on the Review + create page.
|
Refer to Quickstart: Direct web traffic with Azure Application Gateway - Azure portal for more information. |
Ready to Go
-
Make sure Server (backend pool) status is in a Healthy state from the Azure portal page Application Gateway > Backend health.
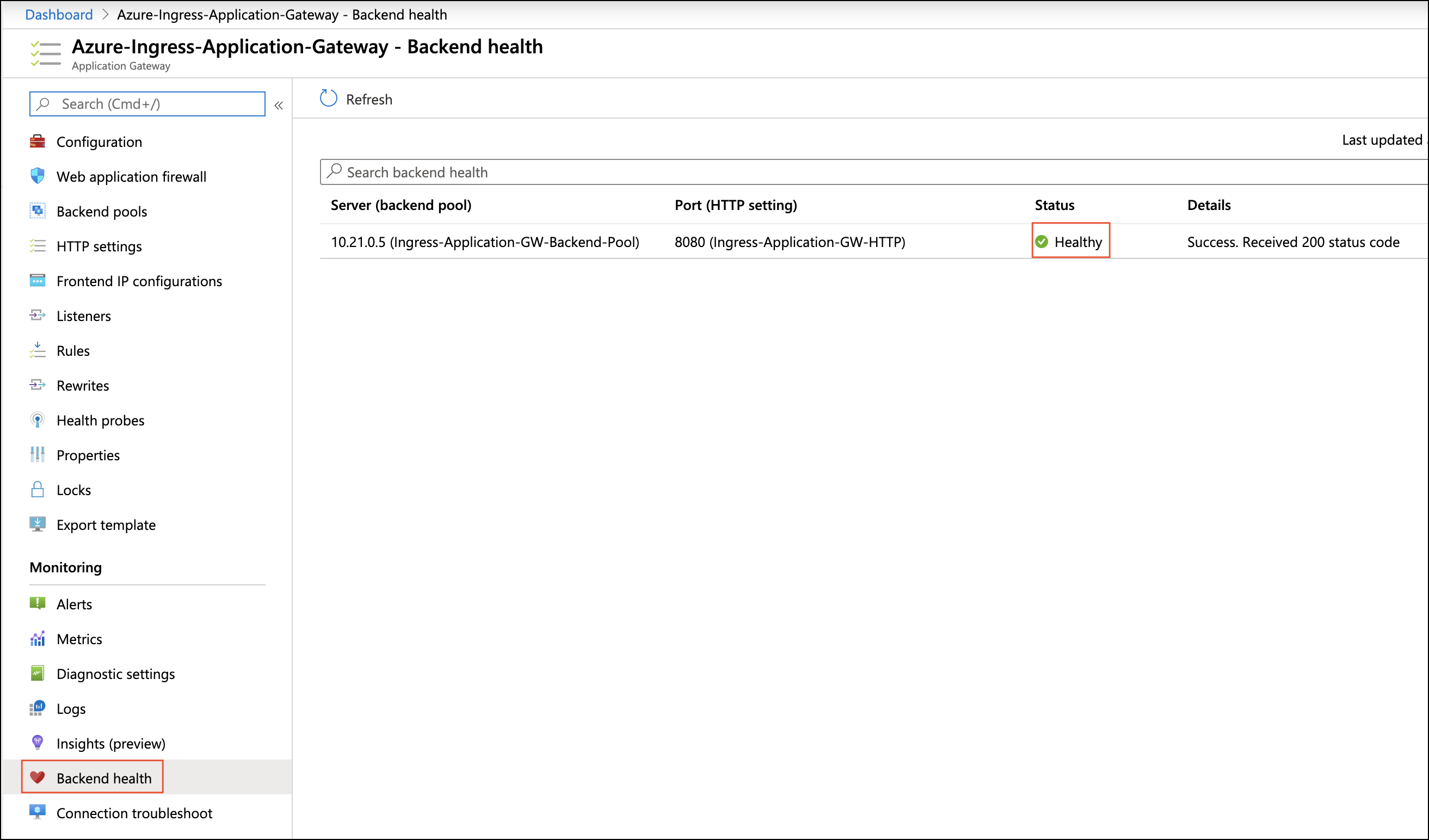
-
Run a http request targeting the Azure Application Gateway Public IP or DNS name.
-
Find the Frontend public IP address of the Azure Application Gateway from the Azure portal page Application Gateway > Overview.
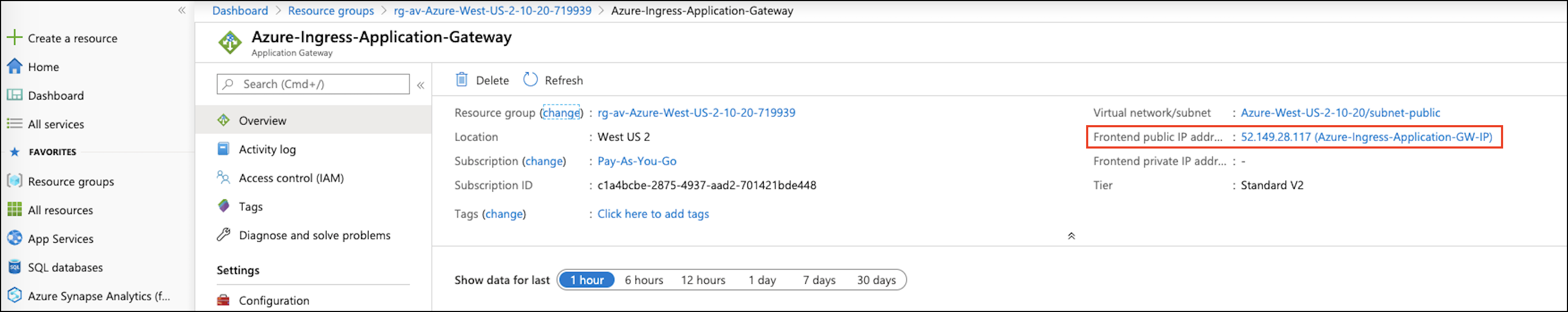
-
Copy the Frontend public IP address of Azure Application Gateway and paste it on a browser from your laptop/PC.
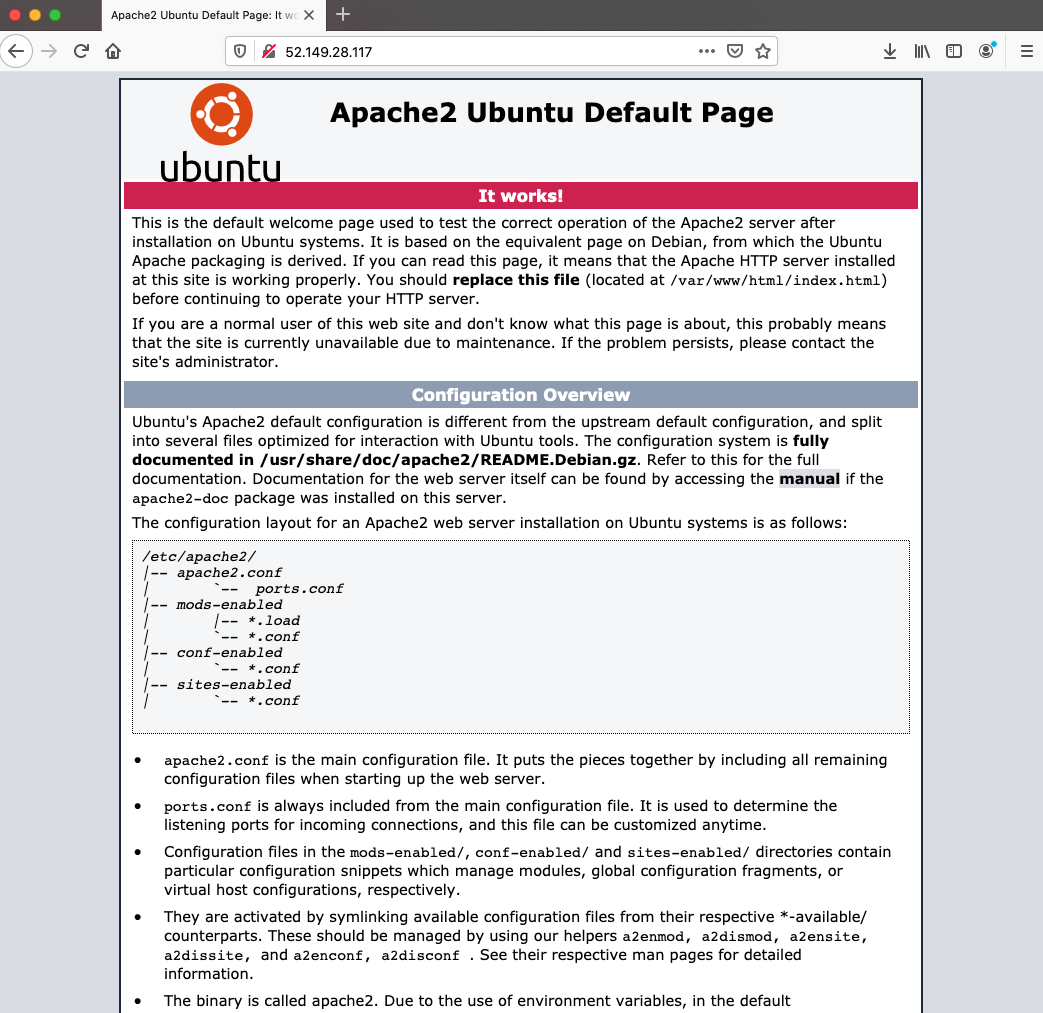
-
Perform tcpdump with port 8080 on Apache2 Web server.
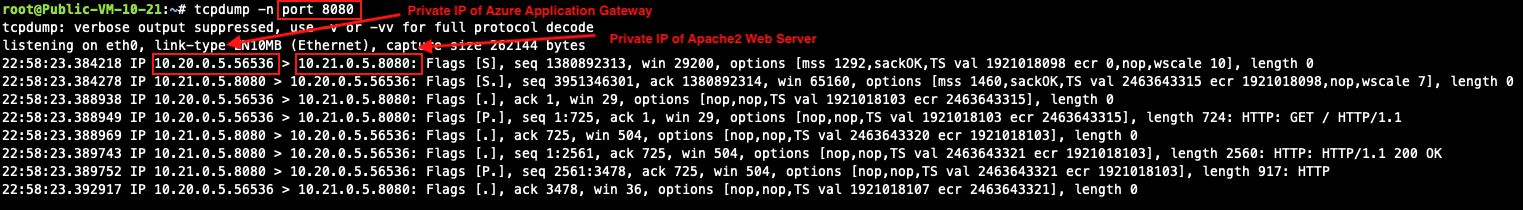
Azure Application Gateway automatically preserves client original IP address in the HTTP header field "X-Forwarded-For (XFF)". Here is an HTTP packet example which is opened with Wireshark tool for your reference:
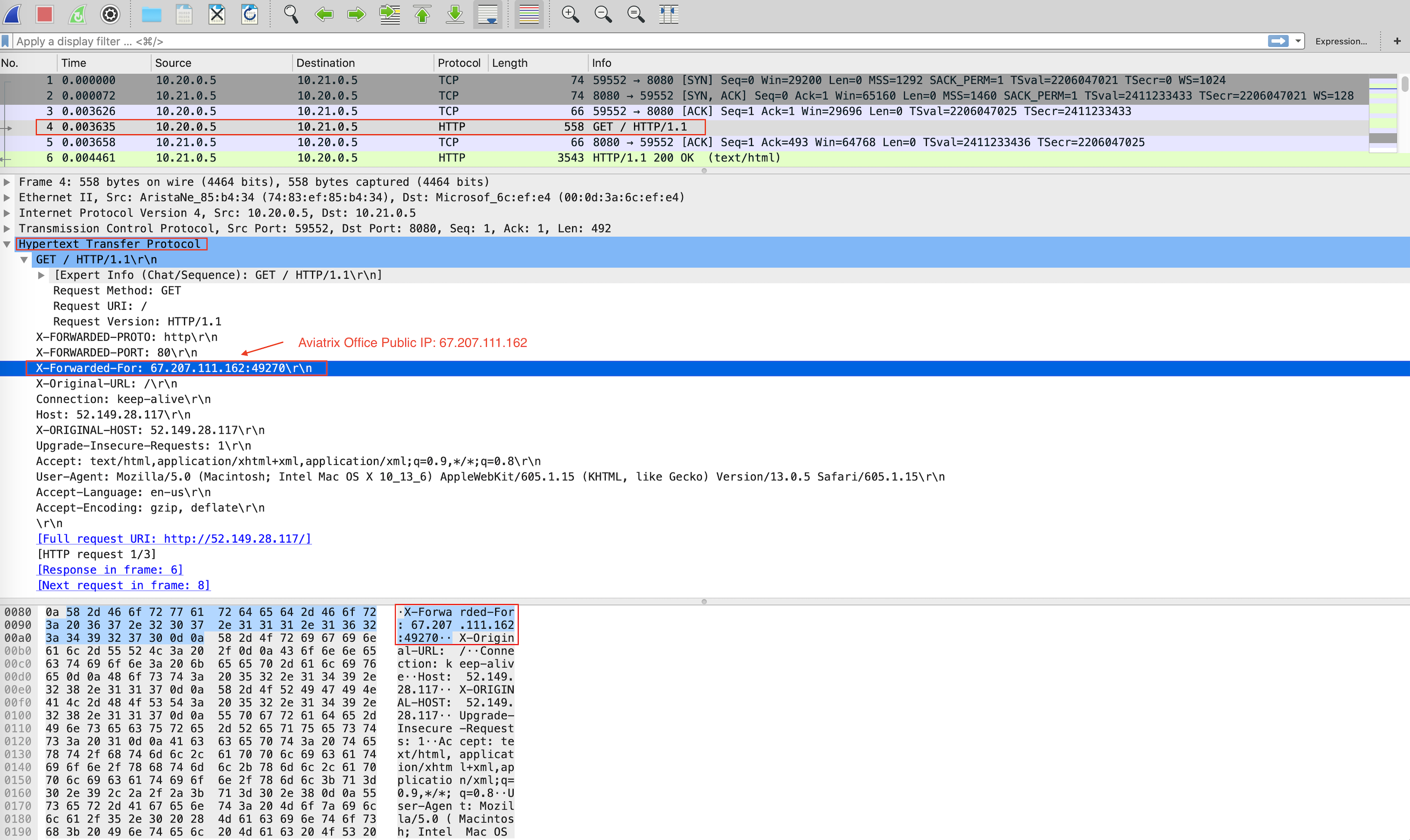
-
Viewing Traffic Log on Firewall
You can view if traffic is forwarded to the firewall instance by logging in to the Palo Alto VM-Series console. Go to Monitor > Logs > Traffic. Perform http/https traffic from your laptop/PC to the public IP or the domain name of Azure Application Gateway.
Capturing Client IP in Logs
To view the client IP address in the access log, follow the instructions in How to save client IP in access logs.
-
Find and open Apache configuration file.
#vim /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
-
In the LogFormat section, add %{X-Forwarded-For}i as follows:
... LogFormat "%{X-Forwarded-For}i %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common ... -
Save your changes.
-
Reload the Apache service.
#systemctl reload apache2
-
Review the public/original client IP on apache2 access log.
