Ingress Protection via Aviatrix Transit FireNet with Palo Alto in GCP
This document describes how to configure ingress in GCP with traffic inspection, deployed directly in Transit FireNet. In this configuration you use the native GCP load balancers in Transit FireNet. These load balancers are created after you enable Transit FireNet as part of the Transit FireNet Workflow for GCP.
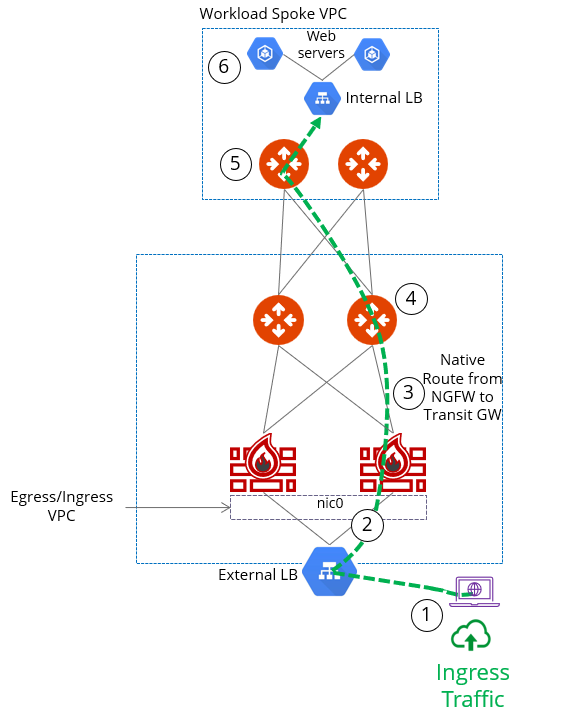
The solution described below shows how to implement network load balancer (NLB)-based ingress with Palo Alto firewalls in GCP.
|
In this NLB-based deployment in GCP, the original source address is preserved. The firewall then has to NAT the traffic source to its LAN interface IP; that’s where the original source IP is rewritten (SNAT). |
This document provides a step-by-step guide for application ingress protection via Aviatrix Transit FireNet using Palo Alto firewalls for Aviatrix Controller version R6.6 and later.
For more information about Transit FireNet, see the following:
Design Considerations
This document describes NLB-based ingress in GCP. However, there are options available for other traffic types. For HTTP/HTTPS load balancing, an HTTP(S) load balancer with Network Endpoint groups could be another option, although this method does not preserve the source IP address until the firewall is reached. For a limited list of supported ports you can also use a TCP proxy-based load balancer with Network Endpoint Groups.
Currently in GCP you cannot place a HTTP(S) or other form of load balancer into a Spoke VPC, as load balancers are not tied to a subnet and would deliver traffic directly to backend services instead of Spoke gateways. A third-party appliance such as F5 could be used to do this in a spoke network if needed.
Deployment Steps
Deploy a Transit FireNet in GCP
Set up a Transit FireNet in GCP and enable centralized egress. For details on setting up Transit FireNet see Transit FireNet Workflow.
Set up Firewall Instances for Egress
-
Enable vendor integration with the firewalls by going to Security > FireNet > FireNet Gateways.
-
Next to the desired Transit FireNet, click the vertical ellipsis
 and select Vendor Integration).
and select Vendor Integration). -
Click the Edit icon
 next to the desired Transit FireNet. In the Edit Transit FireNet dialog, slide the Egress toggle to On.
next to the desired Transit FireNet. In the Edit Transit FireNet dialog, slide the Egress toggle to On.
Verify Health Probe Status
In the GCP console open the Load balancing menu and check the health of the load balancers used by the Transit FireNet. These load balancers were created during the Transit FireNet setup for GCP. There will be one UDP and one TCP load balancer. Backends should show as healthy.
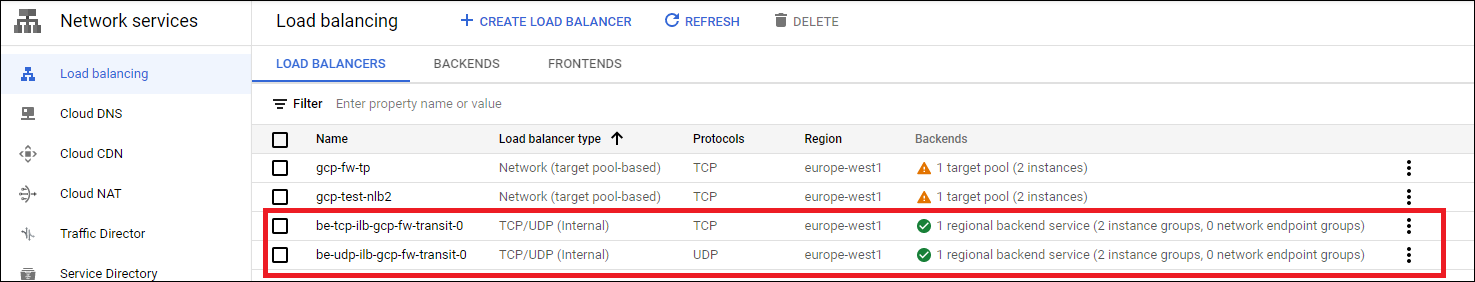
Set up Palo Alto Firewalls for Ingress Load Balancing
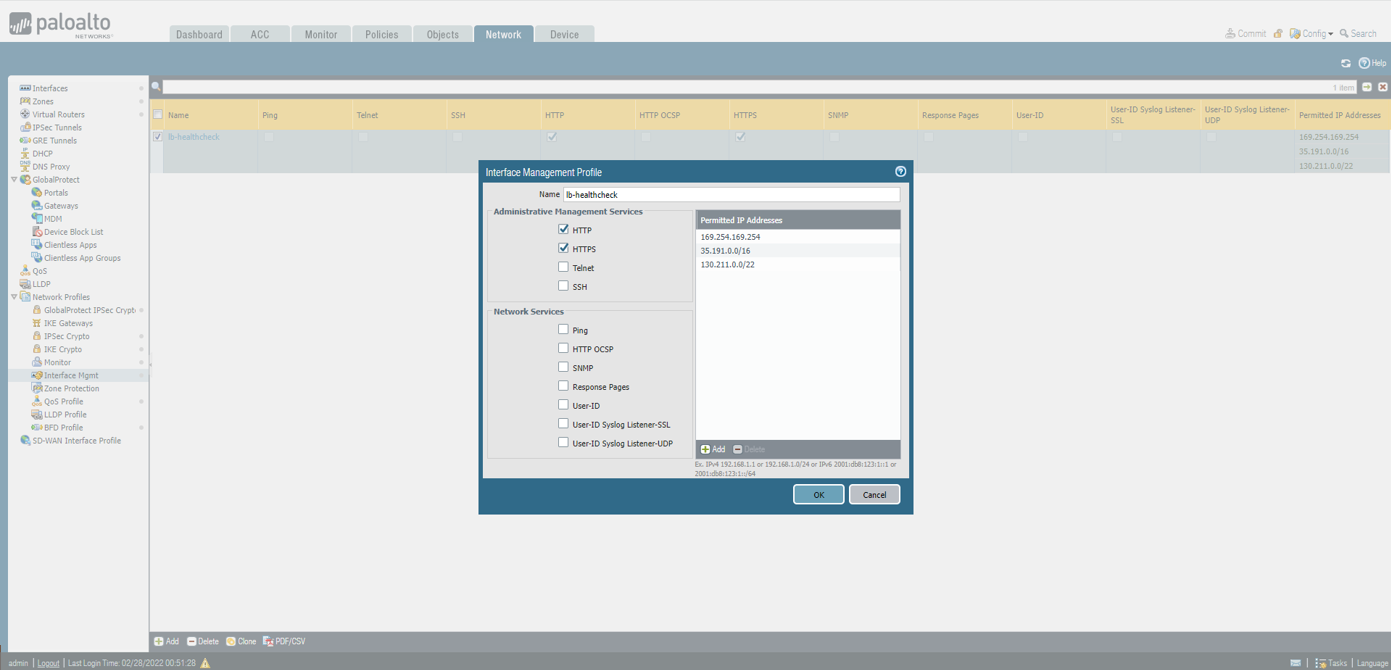
Update Management Profile
Edit the management profile to restrict access to firewall management access over WAN and LAN interfaces to only health probes.
Enable HTTP access since the legacy health probes in GCP only support HTTP and not HTTPS.
The IP address ranges to add are:
-
169.254.169.254 (legacy health probe for External load balancer)
-
35.191.0.0/16 and 130.211.0.0/22 (health probes for Internal load balancer)
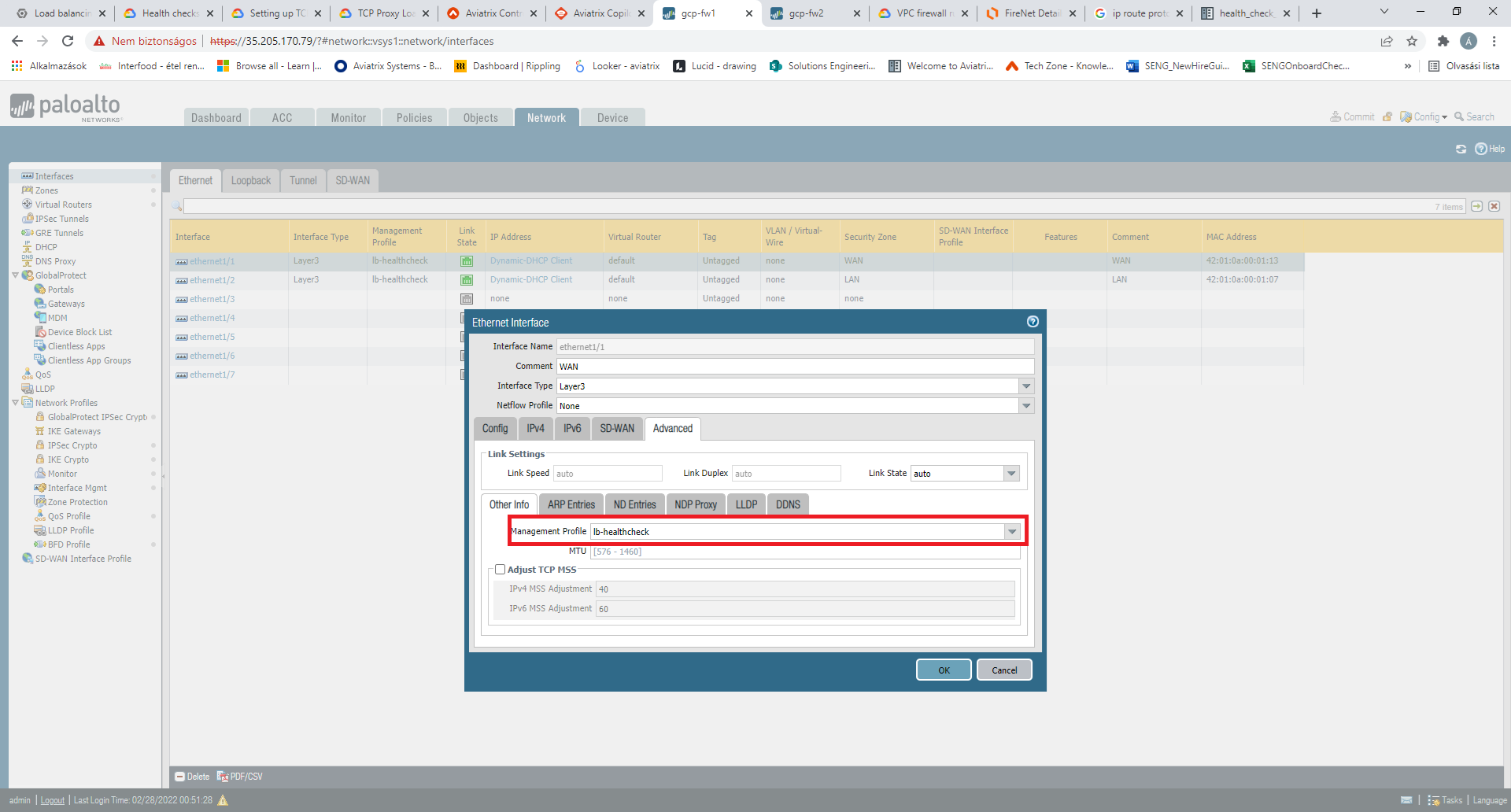
Add the management profile you have updated to the WAN interface of the firewall.
Create Ingress Load Balancer in GCP
Create a Load Balancer in GCP that points to the WAN interface of your firewalls. A Network Load Balancer can terminate any kind of application.
-
Click Create Load Balancer on the Load balancing page.
-
Select TCP Load Balancing > Start Configuration.
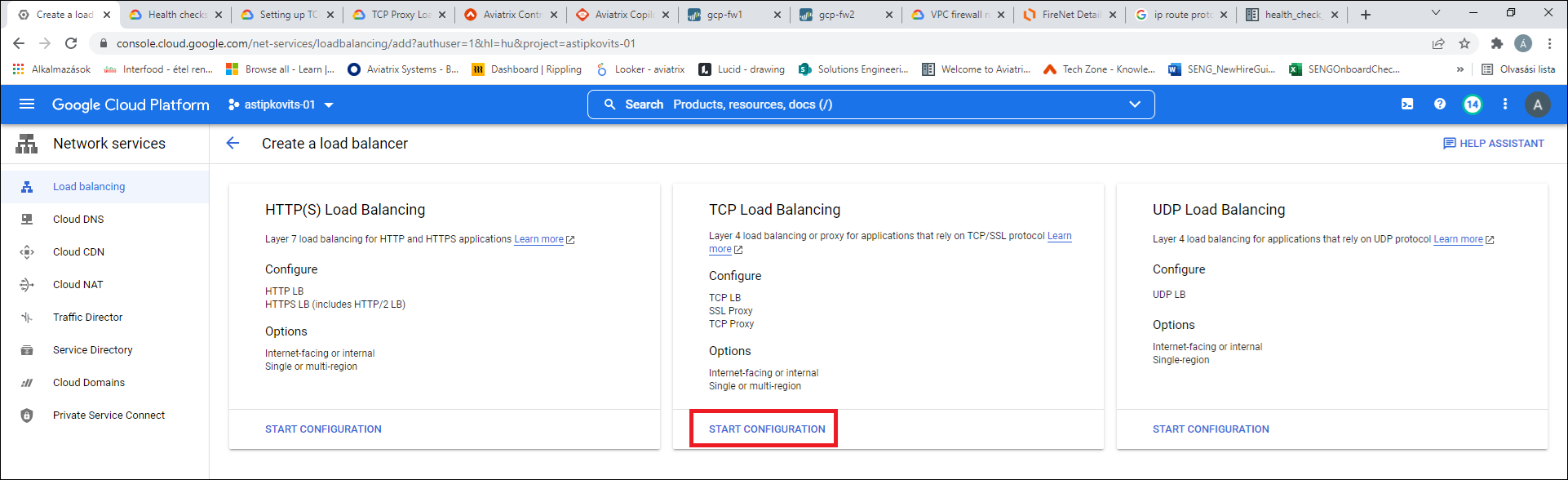
-
Select the load balancer options as shown below: From Internet to my VMs, Single region only, and Target Pool or Target Instance.
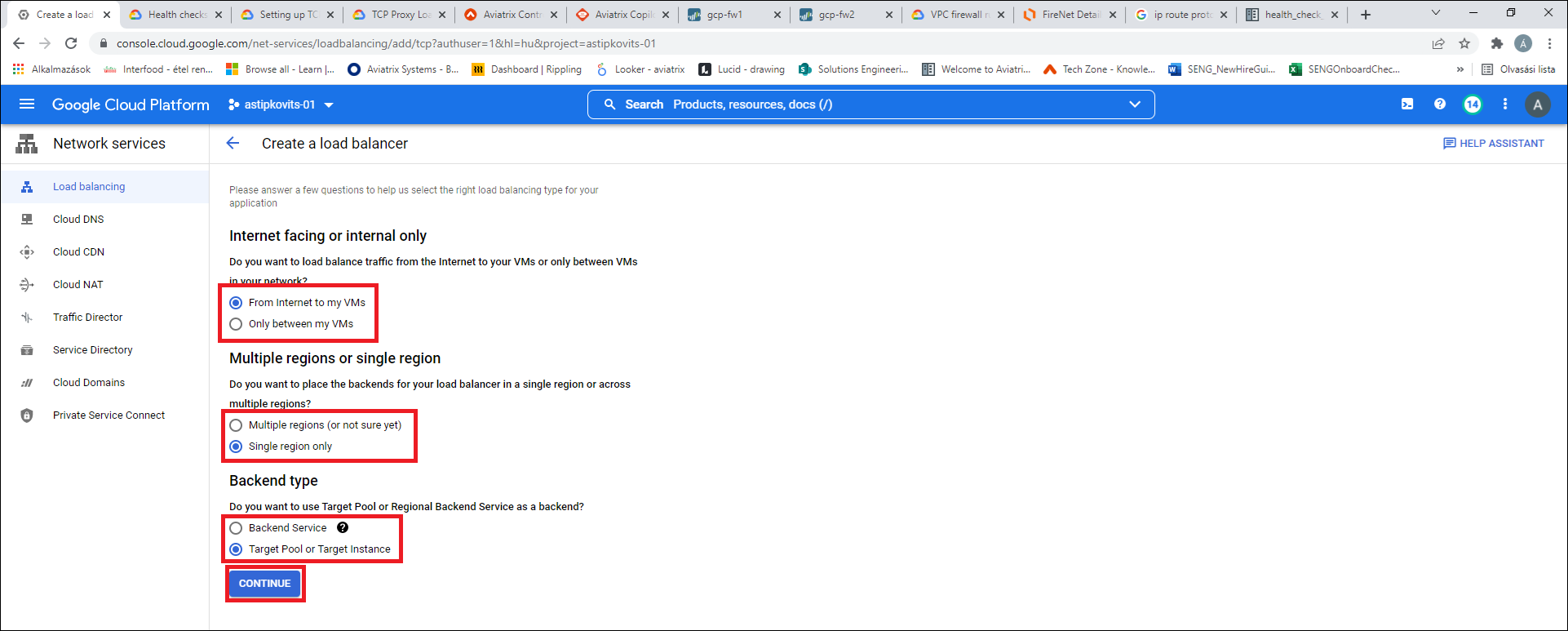
-
Enter a Name and select a Region (must match Transit FireNet’s region), click Select Existing Instances and select the firewall instances.
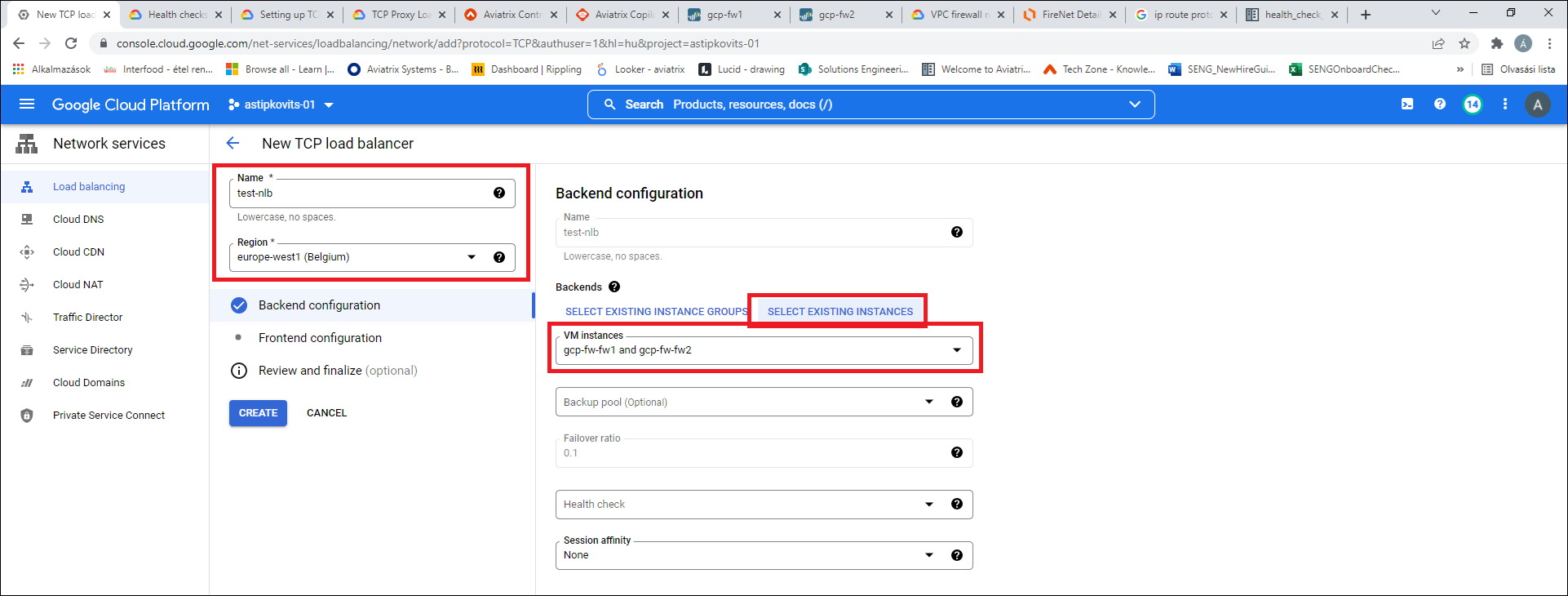
-
In the Health Check area, create a health probe for the Load Balancer. Use port 80 and enter this path: /php/login.php. This path must be set for the health probe to succeed. Click Save.
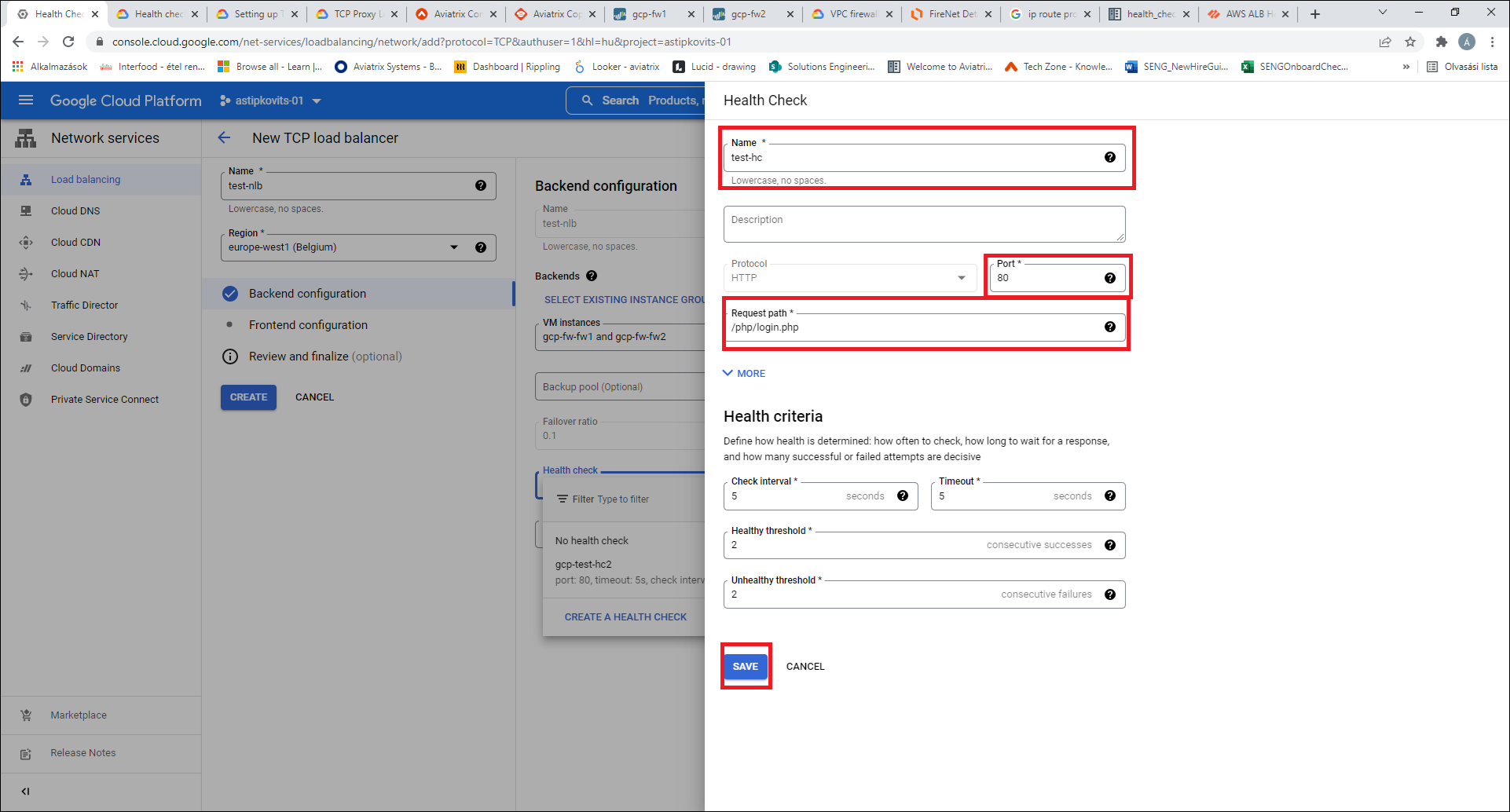
-
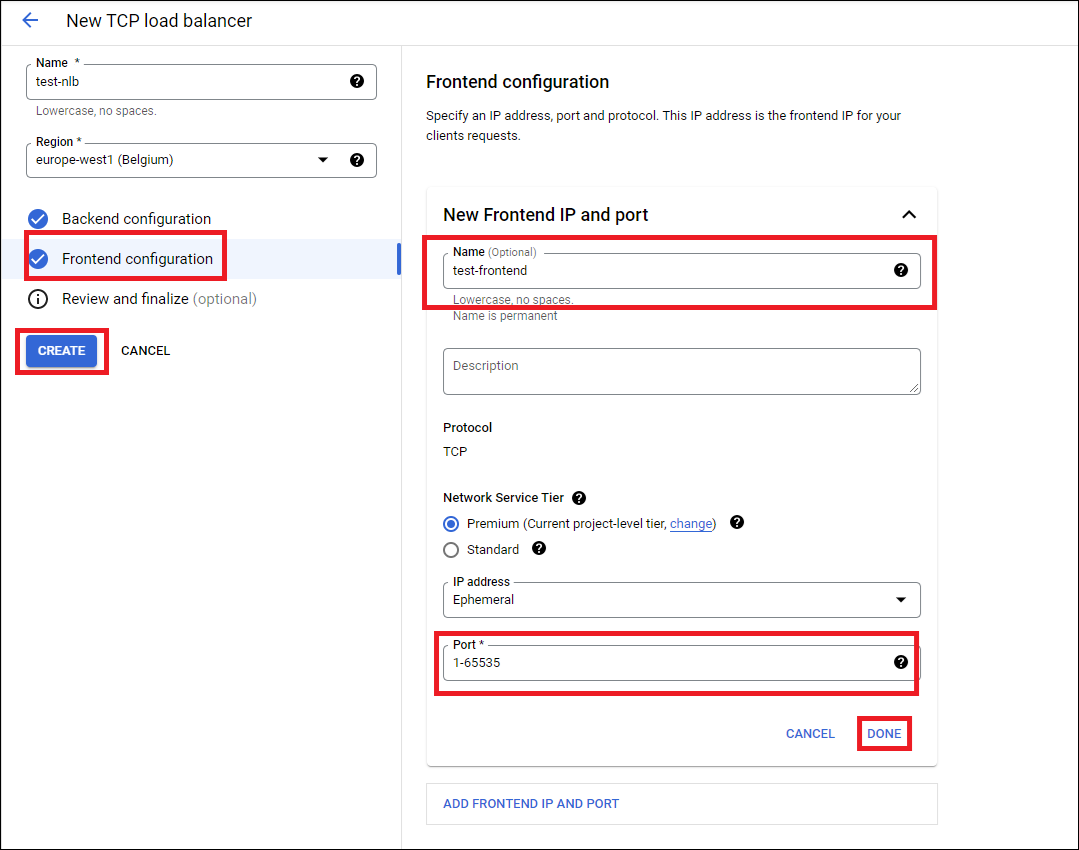
Click Frontend configuration on the Load Balancer Page and set up a frontend for the ingress public IP.
-
Set up one frontend per application (or per public IP needed).
-
Specify the port needed for the application. Note that you cannot modify this port later, so if you are unsure, set up 1-65535 as this allows all ports to be forwarded to the firewall for this IP address.
-
Click Create to create the load balancer.
-
Set up Firewalls for Ingress Application Traffic
Create NAT Rules
Now that the load balancer is created, you must create a NAT rule for the firewall to answer those probes destined for the frontend IP address of the load balancer.
In the firewall UI, create a DNAT rule for each frontend IP, to ensure that the health check will work.
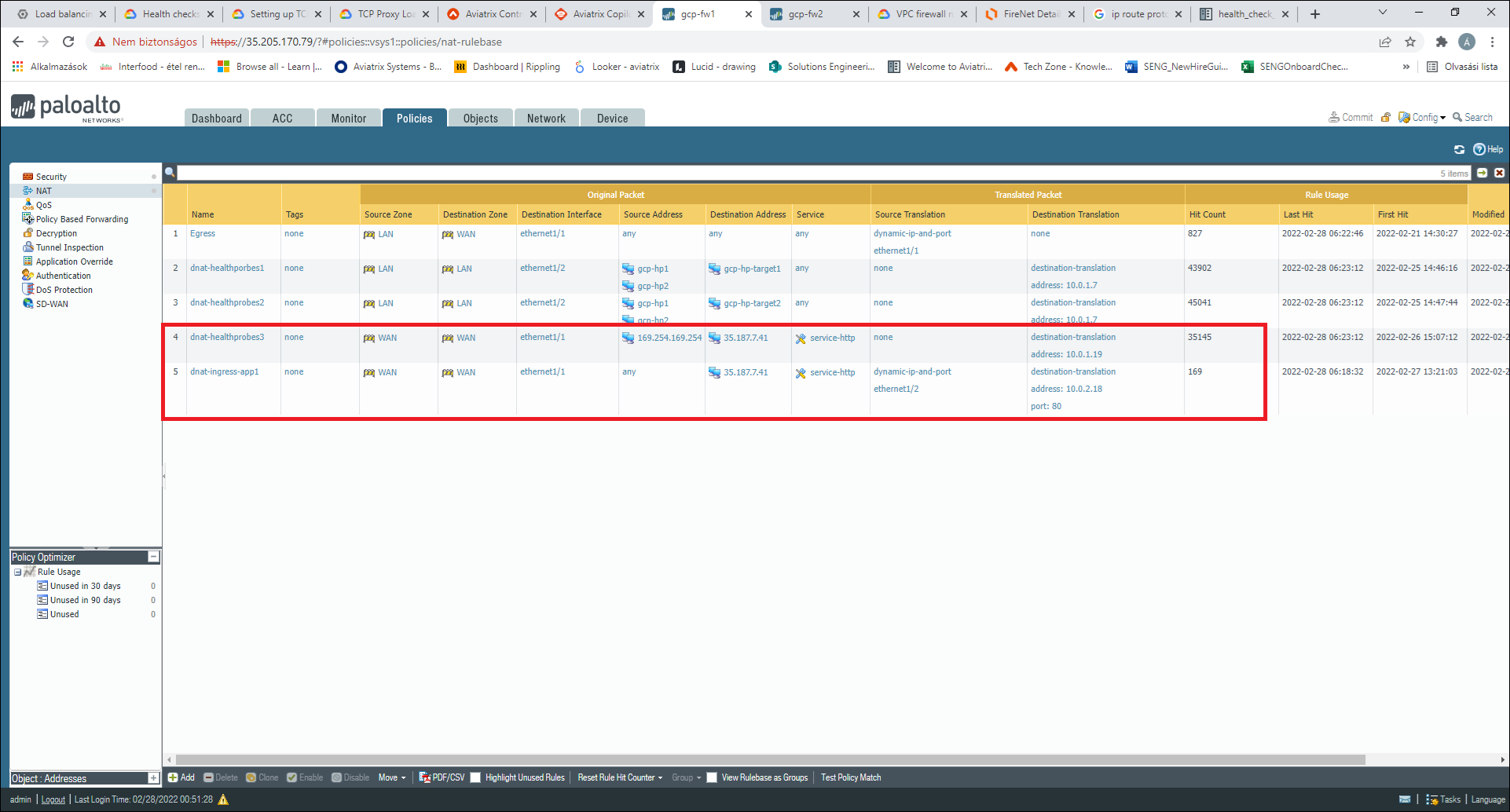
Next, create a DNAT/SNAT rule for each application to DNAT/SNAT traffic to the actual application IP in the Spoke. The following screenshot shows an example for these rules.
This example uses the following parameters:
-
Fronted IP: 35.187.7.41
-
Ingress application port: 80 (this must always be 80 for the health probe NAT rule)
-
Firewall’s WAN interface IP address: 10.0.1.19
-
Application IP in spoke: 10.0.2.18
You need to SNAT traffic to the firewall’s LAN port to make sure returning traffic hits the same firewall.
Make sure you always add the health probe NAT rule above the ingress app rule, as that is more specific in case the application and the health probe use the same port.
Update Firewall Policy
-
Update the security policy on the firewall to enable access to the Frontend IP address of your load balancer from the health probe address (169.254.169.254) using HTTP (this will be the original health probe packet).
-
Set up the firewall’s security policy to enable the application ingress traffic.
Set up GCP Firewall Rules for Ingress
-
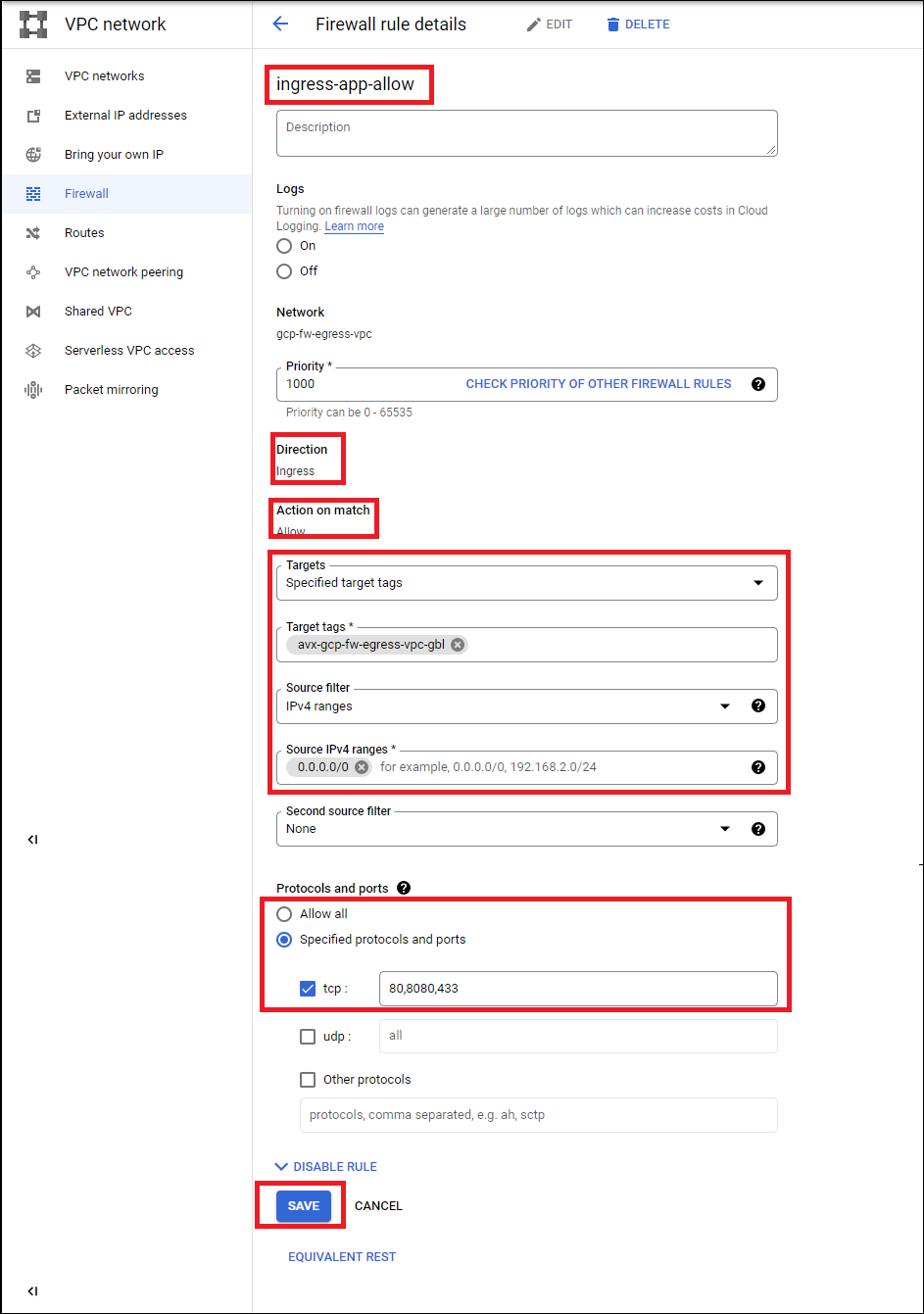
Add an ingress firewall rule to the GCP firewall to allow ingress traffic to the firewall for the application. Use the tag avx-<egress_vpc_name>-gbl for matching the firewall instances. Allow the application’s port from 0.0.0.0/0 in.
-
Use the name of your egress VPC as a parameter in the tag’s <egress_vpc_name>. In the example below the egress VPC name is "gcp-fw-egress-vpc" resulting in the tag name of "avx-gcp-fw-egress-vpc-gbl".
Validate the Setup
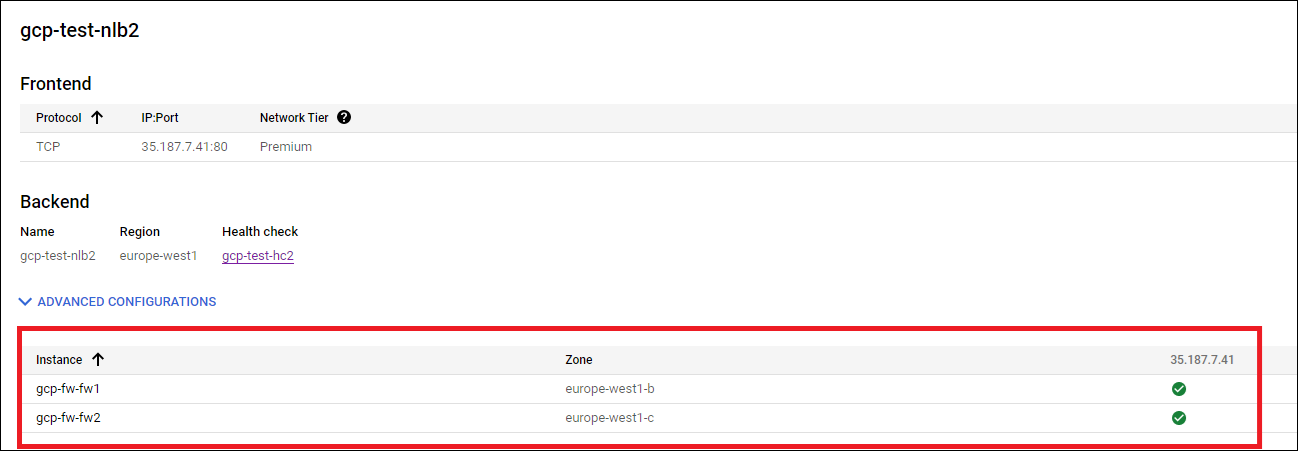
Check that the load balancer in the GCP console shows the backend as healthy for the firewalls. Note that when you reboot a firewall, it might take up to 30 minutes to respond to health checks on port 80.
Initiate traffic from the Internet toward your application hosted in the spoke VPC. To do so, use the frontend IP address of the load balancer you created and the defined frontend port. Your application should respond.