Transit FireNet Workflow for AWS
Aviatrix Transit FireNet allows you to deploy firewall functions for the Aviatrix Multicloud transit architecture. With the Transit FireNet feature, the Firewall Network is integrated into the Aviatrix Transit gateway.
To deploy firewall networks in other CSPs:
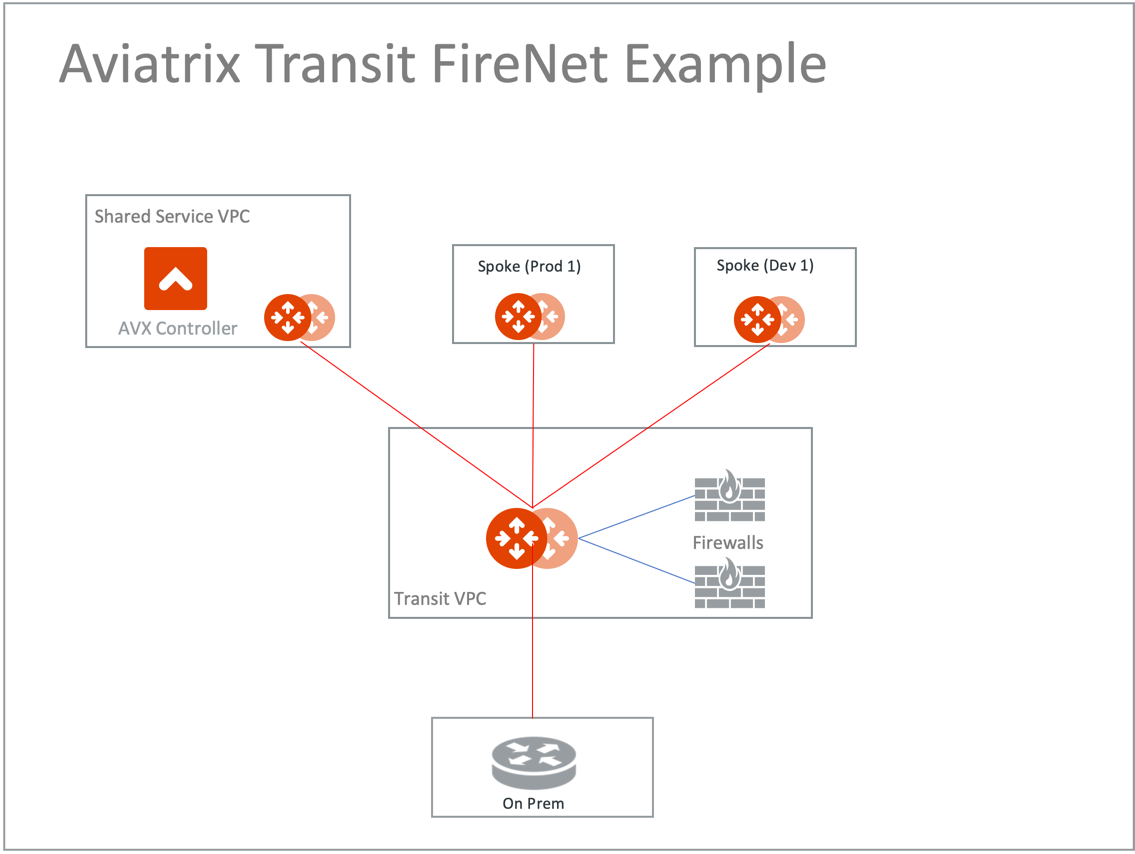
In this example, a transit VPC with Aviatrix Gateways is deployed, and two Spoke Gateways (DEV and PROD) are attached to it.
The transit VPC will have a firewall of a supported vendor (Check Point, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, etc.) deployed in it. See the diagram below for more details.
Once the infrastructure is in place you create a policy to inspect the east-west and north-south traffic.
Create VPCs
VPCs can be created manually on AWS or directly from the Aviatrix Controller.
In this example, VPCs are created following the Useful Tools Create a VPC guidelines.
-
Log in to the Aviatrix Controller with a username and password.
-
Navigate to Useful Tools > Create A VPC.
-
Select AWS as the Cloud Type.
-
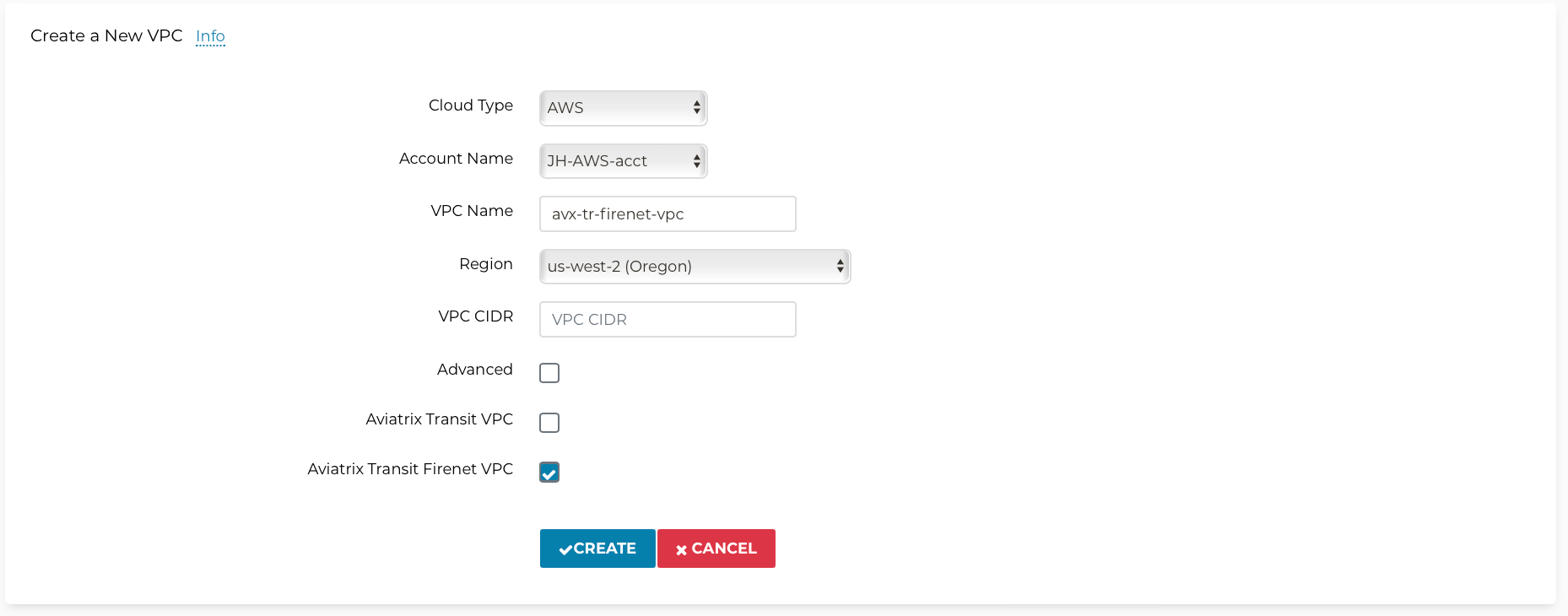
Add one VPC for Transit FireNet Gateway and select the Aviatrix FireNet VPC option as shown below.
-
Create two more VPCs with no option/checkbox selected for Spoke Gateways.
Deploy the Aviatrix Transit Gateway
The Aviatrix Transit Gateway can be deployed using the Transit Gateway Workflow.
Prerequisites for AWS
Transit FireNet builds on the Aviatrix Transit Network solution where Aviatrix gateways are deployed in both the Transit VPC and the Spoke VPCs in AWS. ActiveMesh is enabled by default.
Make sure the deployment meets the following specifications:
-
The minimum size of the Aviatrix Transit Gateway is c5.xlarge.
-
Aviatrix Transit Network must be in Connected mode. Go to Transit Network > Advanced Config > Connected Transit and click Enable.
Procedure
-
Navigate to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup > #1 Launch an Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Select the AWS Cloud Type.
-
Enter a gateway name.
-
Select the AWS Access Account Name.
-
Select a region.
-
Select the VPC ID of the AWS Transit VPC.
-
Select the Public Subnet.
-
Select the C5x.large instance size.
-
Enable High Performance Encryption Mode encryption for higher throughputs (optional).
-
Enable Transit VPC GW HA by navigating to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup → #2 (Optional) Enable HA to an Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Select the Transit gateway and the HA Gateway Subnet.
-
Click Enable.
| The c5.xlarge instance size will be required for High Performance Mode Encryption (for higher throughput). |
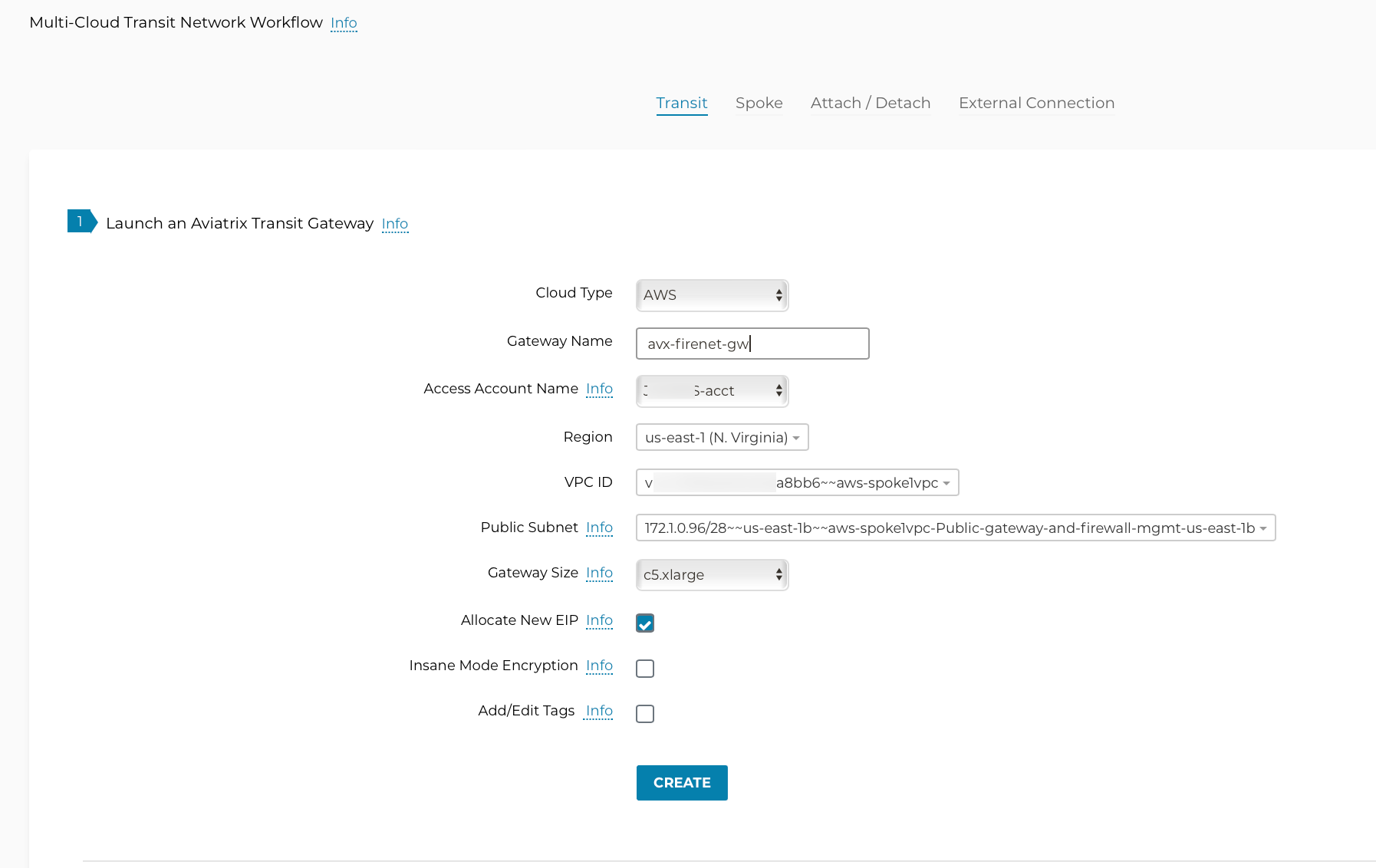
Please see an example below for Transit FireNet GW:
Deploy Spoke Gateways
Now that there is an Aviatrix Transit Gateway, you can deploy Aviatrix Spoke Gateways in the Spoke VPCs using the Aviatrix Spoke Gateway Workflow.
-
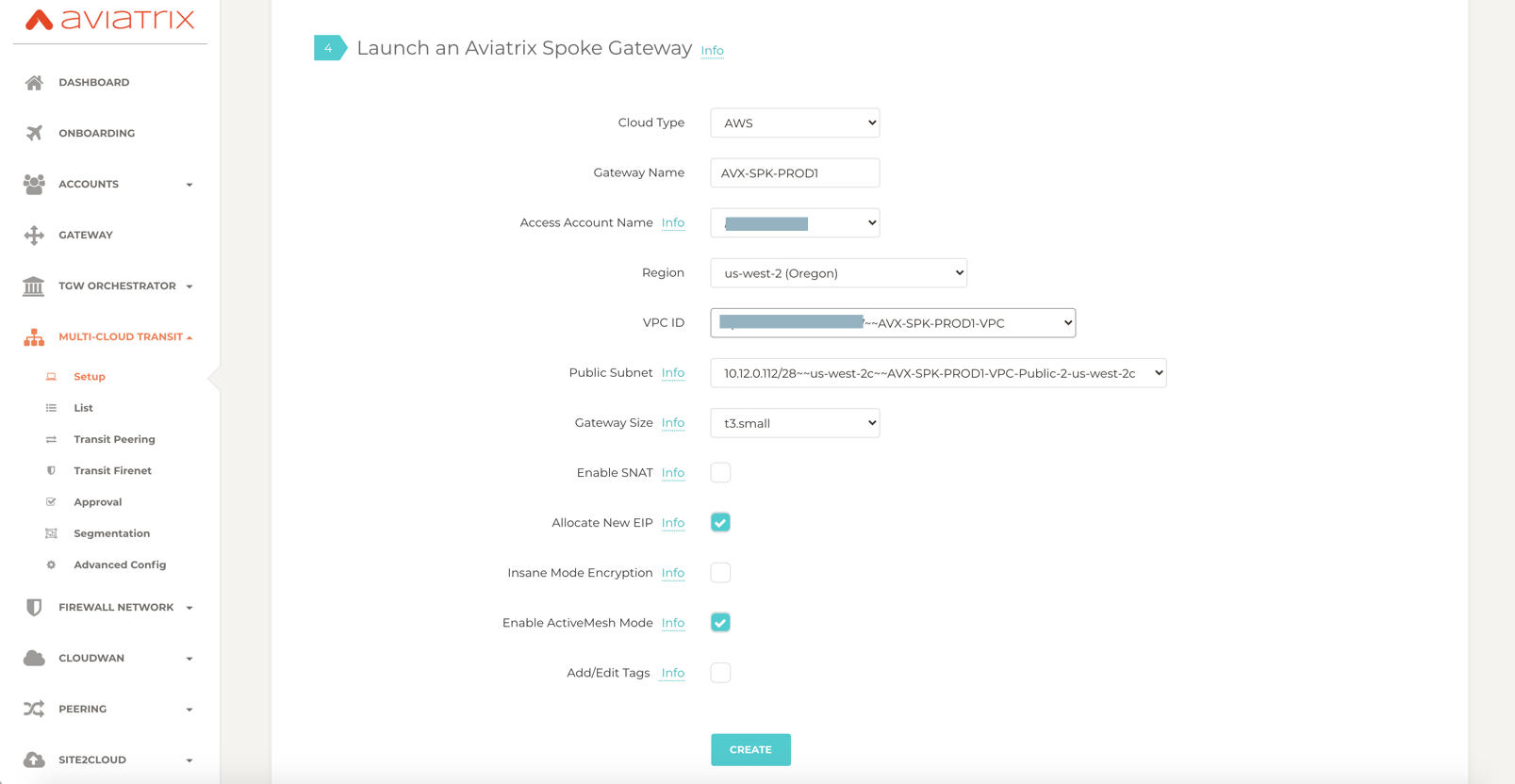
Navigate to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup > Spoke > #1 Launch an Aviatrix Spoke Gateway.
-
Deploy a Spoke Gateway (GW) in each of the spoke VPCs using the correct Account and VPC information.
-
Choose the Public Subnet.
-
Enable Spoke Gateway HA by navigating to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup > Spoke > #5 (Optional) Enable/Disable HA to an Aviatrix Spoke Gateway.
| The c5.xlarge instance size will be required for High Performance Mode Encryption (for higher throughput). |
Attach Spoke Gateways to Transit Network
Now that the Transit and Spoke gateways are deployed, you must connect them.
-
Navigate to Multi-Cloud Transit > Setup > Attach/Detach > #1 Attach Spoke Gateway to Transit Network.
-
Select one Spoke at a time and attach to the Transit Gateway.
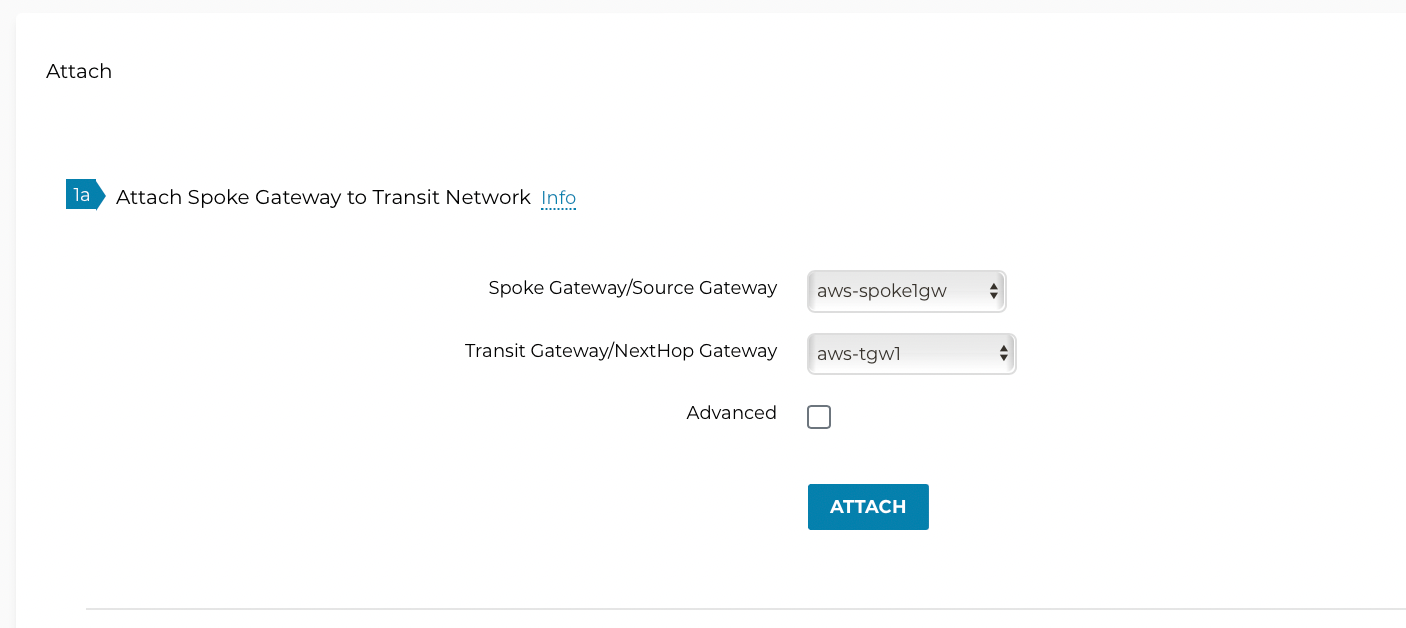
| The Transit Gateway is now attached to the Spoke gateways, but by default the Transit Gateway will not route traffic between Spoke gateways. |
Enable Connected Transit
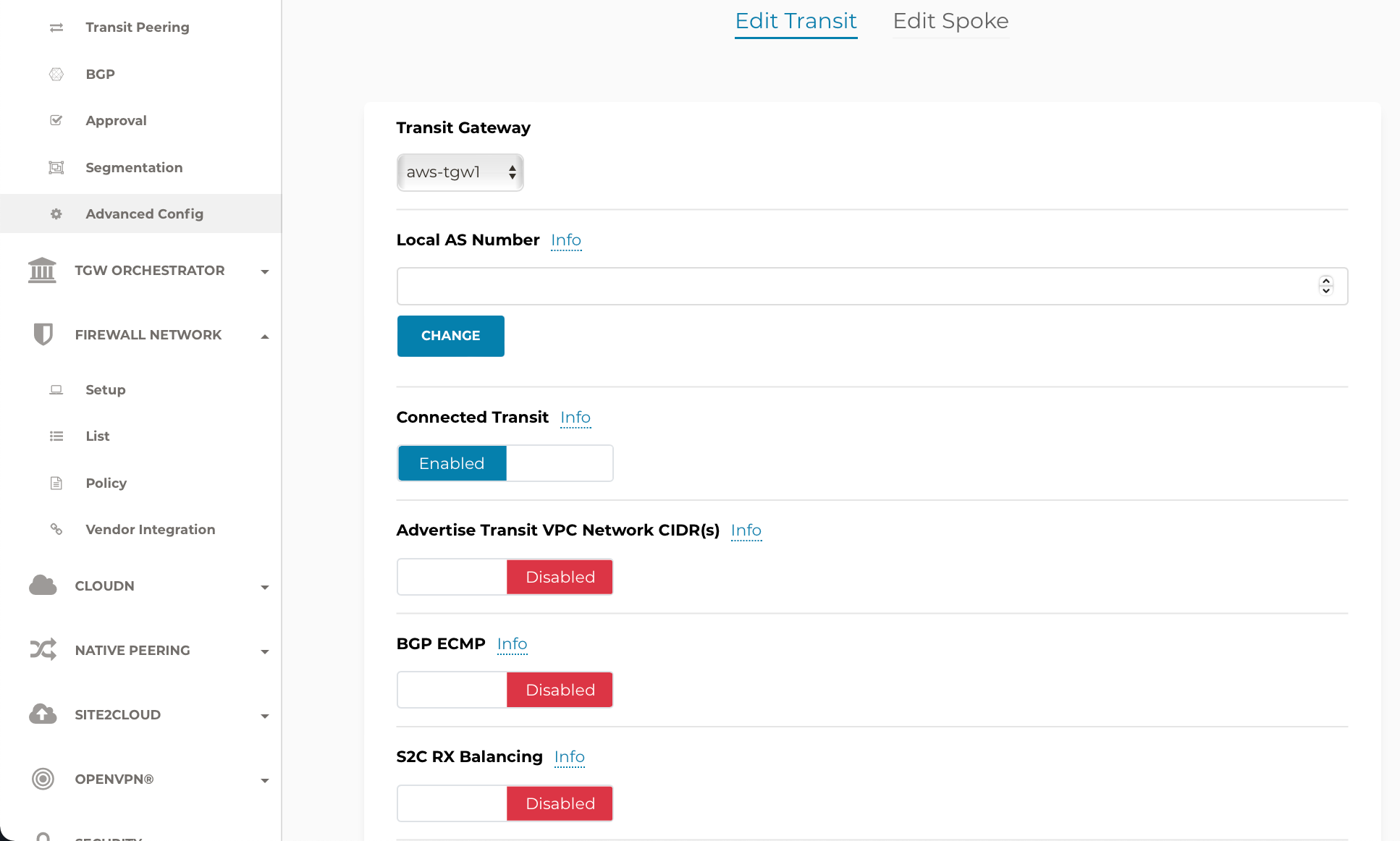
By default, Spoke VPCs are in isolated mode where the Transit will not route traffic between them. To allow the Spoke VPCs to communicate with each other, you must enable Connected Transit by navigating to Multi-Cloud Transit > Advanced Config. Under Edit Transit, select the Transit Gateway and toggle Connected Transit to Enabled.
Configure Transit Firewall Network
Now that Transit and Spoke Gateways have been deployed, you must deploy and enable the Firewall for traffic inspection.
-
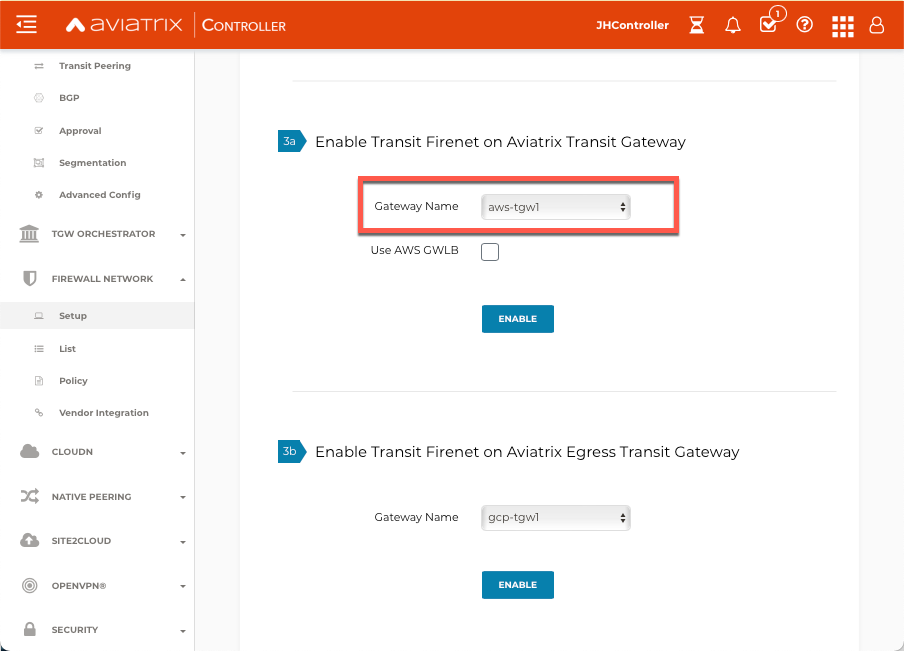
Navigate to Firewall Network > Setup > Transit Firenet > #3a Enable Transit FireNet on Aviatrix Transit Gateway.
-
Choose the Aviatrix Transit Gateway and click Enable.
-
If you are setting up Centralized FireNet, under 3c on the same page select the Primary and Secondary FireNets from the lists and click Attach.
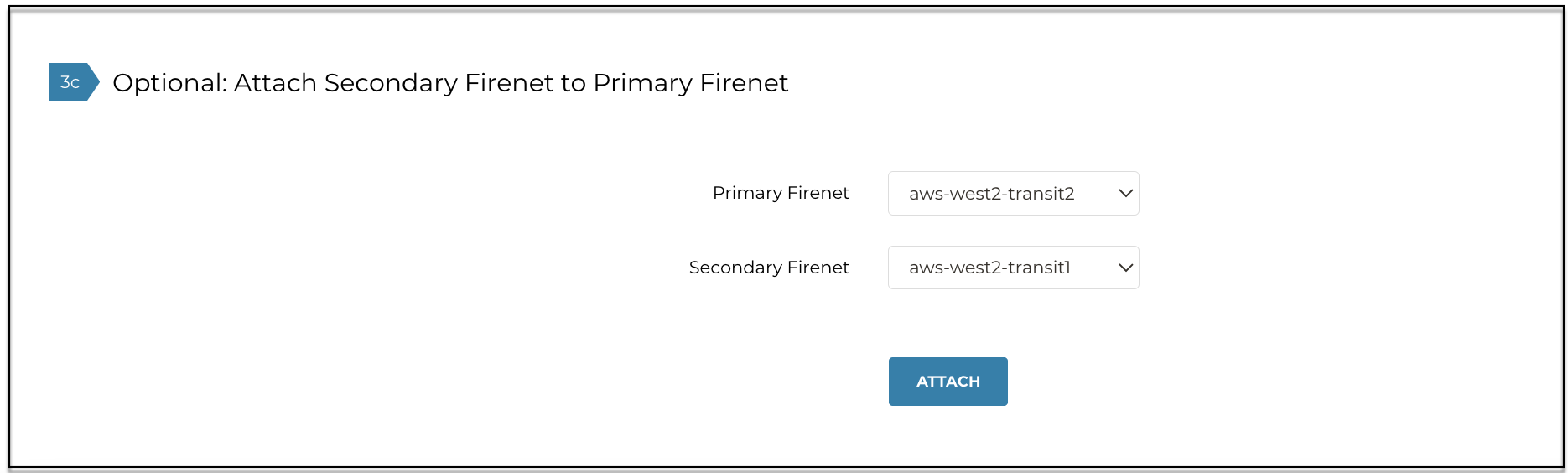
| Ensure that the Centralized FireNet prerequisites are met before attaching. |
-
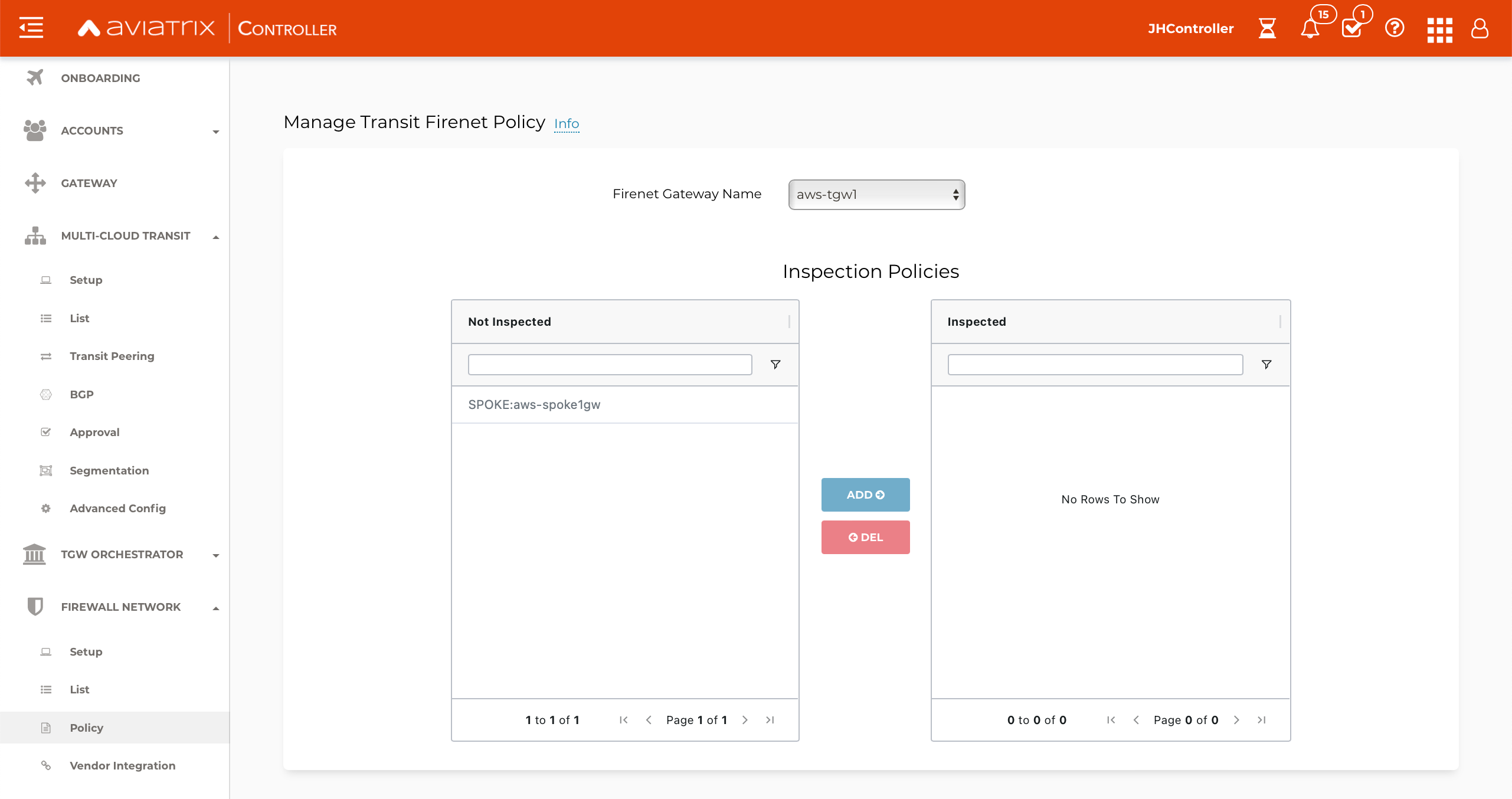
Navigate to Firewall Network > Policy > Manage FireNet Policy.
-
Add Spokes to the Inspected box for traffic inspection.
| By default, FireNet inspects ingress (internet to VPC) and east-west traffic (VPC to VPC) only. |
Centralized FireNet
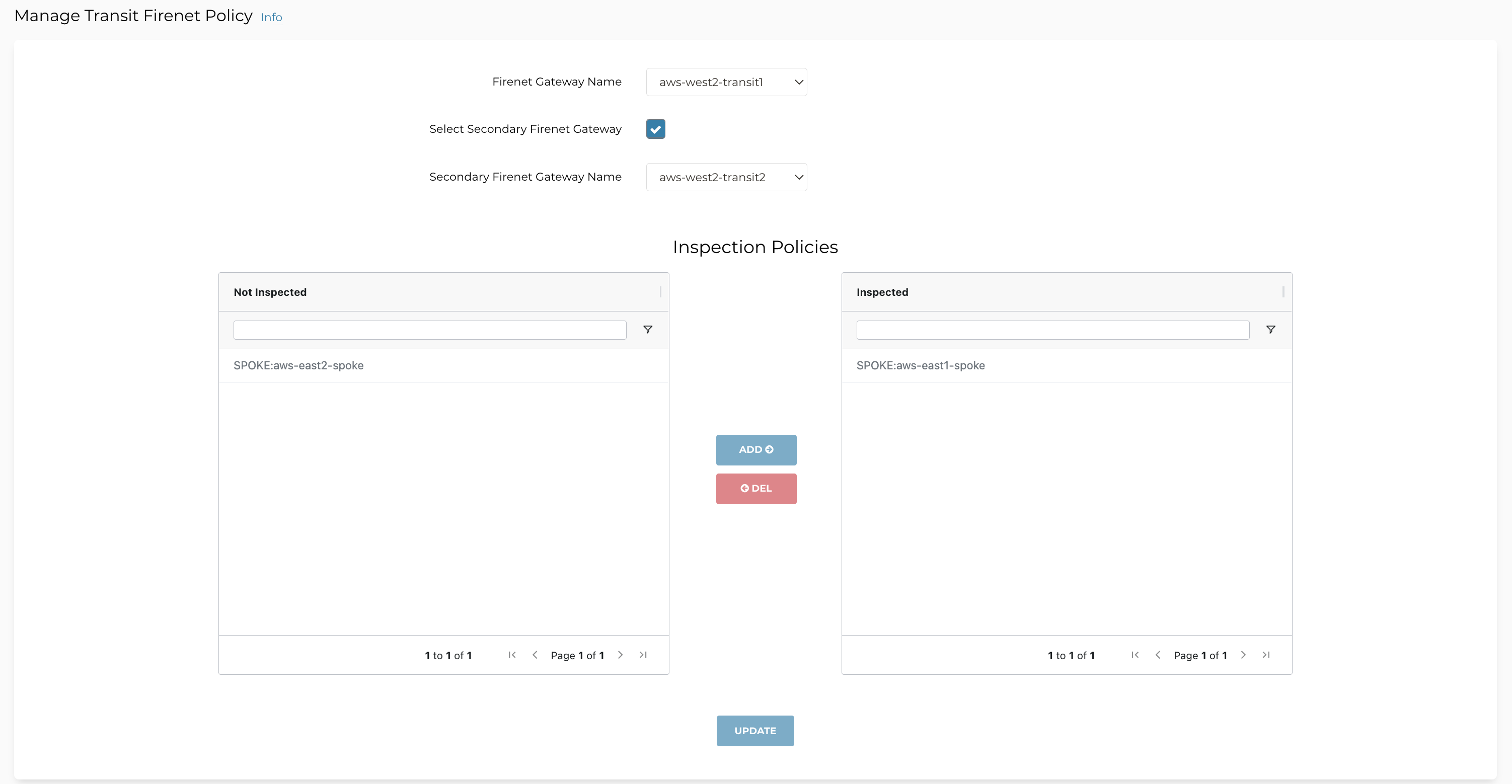
If you have configured Centralized FireNet, when you select a Transit FireNet from the Transit Gateway Name field (that functions as a Primary FireNet), the Select Secondary FireNet checkbox displays if there are Secondary FireNets attached to the Primary, as shown below.
-
Select a Secondary FireNet from the Secondary FireNet Gateway Name list and configure the inspection policies accordingly for the Secondary FireNet.
-
Click Update.
These inspection policies are then propagated to the Primary FireNet.
|
Inspecting Secondary FireNet policies that start with PEERING will only work if:
|
Subscribe to Firewall Vendor in AWS Marketplace
At this point, FireNet functionality on Transit Gateway is enabled and FireNet policy is created for spokes. It is time to subscribe the firewall vendor and deploy the firewall. As indicated in the Aviatrix Controller at Firewall Network > Setup > Firewall, you must subscribe to the supported firewall vendor in your AWS marketplace using an access account onboarded to the Controller.
| Please subscribe to the firewall but do not launch the firewall. |
Launch and Associate Firewall Instance
This approach is recommended if this is the first Firewall instance to be attached to the gateway.
This step launches a Firewall instance and associates it with one of the FireNet gateways.
|
The Firewall instance and the associated Aviatrix FireNet gateway above must be in the same AZ, and we recommend that the Management Interface Subnet and Egress (untrust dataplane) Interface Subnet not be in the same subnet. An EC2 VM instance will be required in AWS, and ICMP should be allowed in the security group. |
Launch and Attach
In the Aviatrix Controller navigate to Firewall Network > Setup > Firewall > Step 2a. Provide all the required input as shown in the table and click Launch.
| The vendor’s firewall may take some time after launch to be available. |
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
VPC ID |
The Security VPC created in Step 1. |
Gateway Name |
The primary FireNet gateway. |
Firewall Instance Name |
The name that will be displayed on AWS Console. |
Firewall Image |
The AWS AMI that you have subscribed in Step 2. |
Firewall Image Version |
Firewall instance current supported software versions. |
Firewall Instance Size |
Firewall instance type. |
Management Interface Subnet. |
Select the subnet whose name contains "gateway and firewall management" |
Egress Interface Subnet |
Select the subnet whose name contains "FW-ingress-egress". |
Username |
Applicable to Azure deployment only. "admin" as a username is not accepted. |
Password |
Applicable to Azure deployment only. |
Key Pair Name (Optional) |
The .pem file name for SSH access to the firewall instance. |
Attach (Optional) |
By selecting this option, the firewall instance is inserted in the data path to receive packet. If this is the second firewall instance for the same gateway and you have an operational FireNet deployment, you should not select this option as the firewall is not configured yet. You can attach the firewall instance later at Firewall Network → Advanced page. |
Advanced (Optional) |
Click this selection to allow Palo Alto firewall bootstrap files to be specified. |
IAM Role |
In advanced mode, create an IAM Role on the AWS account that launched the FireNet gateway. Create a policy to attach to the role. The policy is to allow access to "Bootstrap Bucket". |
Bootstrap Bucket Name |
In advanced mode, specify a bootstrap bucket name where the initial configuration and policy file is stored. |
Firewall Specifications for AWS
Check Point Specifications
The Check Point firewall instance has two interfaces as described below.
| CheckPoint VM instance interfaces | Description | Inbound Security Group Rule |
|---|---|---|
eth0 (on subnet -Public-FW-ingress-egress-AZ-a) |
Egress or Untrusted interface (Egress interface is used as the management interface) |
Controller version lower than 7.0.1577: Allow ALL from 0.0.0.0/0 Controller version 7.0.1577 and above: TCP 443, TCP 22 |
eth1 (on subnet -dmz-firewall) |
LAN or Trusted interface |
Allow ALL (Do not change) |
Note that firewall instance eth1 is on the same subnet as FireNet gateway eth2 interface.
| Launching Check Point firewall instances from the Aviatrix Controller automatically initiates Check Point’s onboarding process. For initial login information, go to Credentials for Checkpoint Initial Login. You must be registered to access the Aviatrix Customer Support website. If you are not already registered, you can sign up at https://support.aviatrix.com. |
| Repeat the Launch and Attach procedure to launch the second firewall instance to associate with the HA FireNet gateway. Or repeat this step to launch more firewall instances to associate with the same FireNet gateway. |
Follow the Check Point Example to launch the Check Point security gateway in AWS.
Palo Alto VM-Series Specifications
The Palo Alto instance has three interfaces as described below.
| Palo Alto VM instance interfaces | Description | Inbound Security Group Rule |
|---|---|---|
eth0 (on subnet -Public-FW-ingress-egress-AZ-a) |
Egress or Untrusted interface |
Allow ALL |
eth1 (on subnet -Public-gateway-and-firewall-mgmt-AZ-a) |
Management interface |
Controller version lower than 7.0.1577: Allow SSH, HTTPS, ICMP, TCP 3978 Controller version 7.0.1577 and above: TCP 443 is allowed from the Controller’s public or private IP; TCP 3978 is allowed from the Controller’s public or private IP with the description "Panorama access, please replace with the correct IP"; and ICMP is allowed from the Controller IP. |
eth2 (on subnet -dmz-firewall) |
LAN or Trusted interface |
Allow ALL (Do not change) |
Note that firewall instance eth2 is on the same subnet as the FireNet gateway eth2 interface.
| For Panorama managed firewalls, you need to prepare Panorama first and then launch a firewall. When a VM-Series instance is launched and connected with Panorama, you need to apply a one time "commit and push" from the Panorama console to sync the firewall instance and Panorama. |
| If VM-Series are individually managed and integrated with the Controller, you can still use Bootstrap to save initial configuration time. Export the first firewall’s configuration to bootstrap.xml, create an IAM role and Bootstrap bucket structure as indicated above, then launch additional firewalls with IAM role and the S3 bucket name to save the time of the firewall manual initial configuration. |
Follow Palo Alto Network (VM Series) Example to launch VM Series firewall in AWS.
FortiGate Specifications
The FortiGate Next Generation Firewall instance has two interfaces as described below.
| Fortigate VM instance interfaces | Description | Inbound Security Group Rule |
|---|---|---|
eth0 (on subnet -Public-FW-ingress-egress-AZ-a) |
Egress or Untrusted interface (used as the management interface) |
Controller version lower than 7.0.1577: Allow ALL Controller version 7.0.1577 and higher: TCP 443 is allowed from the Controller’s public or private IP |
eth1 (on subnet -dmz-firewall) |
LAN or Trusted interface |
Allow ALL (Do not change) |
| Firewall instance eth1 is on the same subnet as FireNet gateway eth2 interface. |
| FortiGate bootstrap configuration in AWS is supported. |
Follow the FortiGate Example to launch FortiGate in AWS.
Associate an Existing Firewall Instance
This step is the alternative to Launch and Associate Firewall Instance. If you already launched the firewall (Check Point, Palo Alto Network or Fortinet) instance from AWS Console, you can still associate it with the FireNet gateway.
In the Aviatrix Controller navigate to Firewall Network > Setup > Firewall > Step 2b and associate a firewall with the correct FireNet Gateway.
| An EC2 VM instance will be required in AWS, and ICMP should be allowed in the security group. |
Example Setup for "Allow All" Policy
After a firewall instance is launched, wait 5-15 minutes for it to become available. Time varies for each firewall vendor. In addition, please follow example configuration guides as below to build a simple policy on the firewall instance for a test validation that traffic is indeed being routed to firewall instance.
(Optional) Vendor Firewall Integration
Vendor integration dynamically updates firewall route tables. The use case is for networks with non-RFC 1918 routes that require specific route table programming on the firewall appliance.
-
In the Aviatrix Controller, navigate to Firewall Network > Vendor Integration > Firewall.
-
Select the Firewall Vendor Type and fill in the Firewall details of your Firewall instance.
-
Click Save.
-
You can click Show or Sync to show the integration details or sync the configuration with the firewall.
Verification
There are multiple ways to verify if Transit FireNet is configured properly:
-
Aviatrix Flightpath - Control-plane Test
-
Ping/Traceroute Test between Spoke VPCs (East-West) - Data-plane Test
Flight Path Test for FireNet Control-Plane Verification
Flight Path is a powerful Aviatrix troubleshooting tool which allows users to validate the control-plane and gives visibility of end to end packet flow.
-
In the Aviatrix Controller navigate to Troubleshoot→ Flight Path
-
Provide the Source and Destination Region and VPC information
-
Select ICMP and Private subnet, and Run the test
|
An EC2 VM instance will be required in AWS, and ICMP should be allowed in the security group. |
Ping/Traceroute Test for FireNet Data-Plane Verification
Once the control-plane is established and no problems are found in security or routing polices, data-plane validation needs to be verified to make sure traffic is flowing and not blocked anywhere.
There are multiple ways to check the data-plane:
-
SSH to Spoke EC2 instance (e.g. DEV1-VM) and ping the other Spoke EC2 to instance (e.g PROD1-VM) to make sure there is no traffic loss in the path.
-
Ping/traceroute capture can also be performed from Aviatrix Controller. Navigate to Troubleshoot > Diagnostics and perform the test.