Multicloud Transit Integration with AWS VGW Workflow
Aviatrix automates the process of discovering and connecting to AWS VGW. The instruction below is for connecting Aviatrix Transit Gateway to AWS VGW.
Before executing this step, a VGW must have already been created on the AWS console.
In the AWS console, select the VGW ID in the dropdown menu.
As a result of this step, a Customer Gateway and a Site2Cloud Connection between the VGW to the Aviatrix Transit Gateway will be automatically created. The Site2Cloud IPsec tunnel establishes a BGP session to exchange routes between on-prem and the cloud. You also can view them under Customer Gateways and Site-to-Site VPN Connections of the AWS console.
| You are responsible for building the connection between VGW and on-prem. The connection is either over the Internet, over Direct Connect, or both. |
We support two patterns of connections: Detached VGW and Attached VGW. The VGW should not be attached to the Transit VPC/VNet.
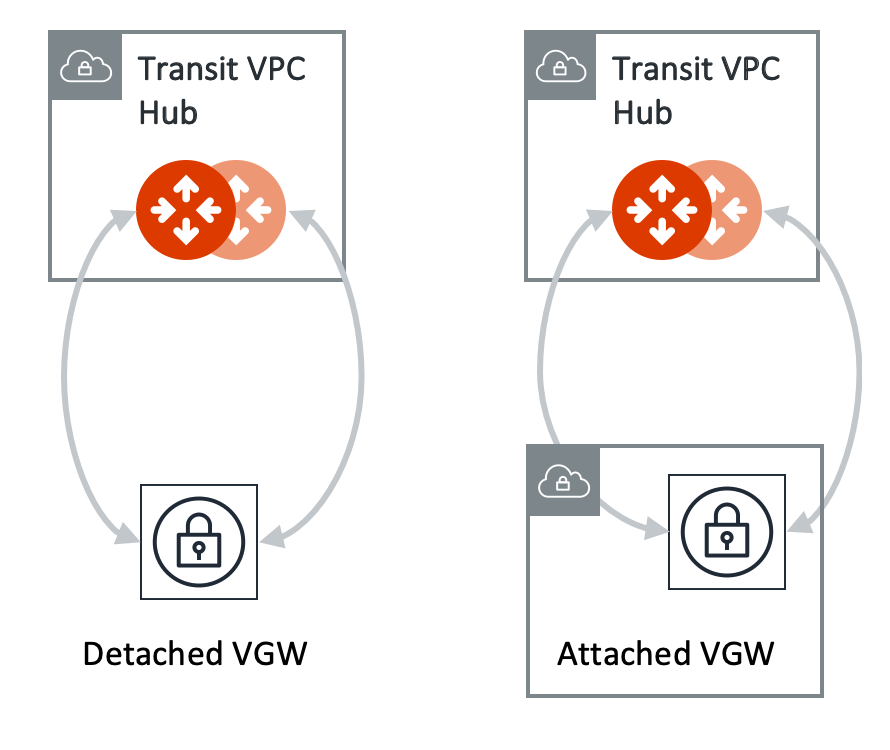
Connecting Transit Gateway to AWS VGW
Connect to an AWS Virtual Private Gateway (VGW).
| This procedure assumes the AWS VGW is already deployed in the Transit VPC. |
To connect the Transit Gateway to AWS VGW (VPN Gateway):
-
Go to Networking > Connectivity > External Connections (S2C) tab.
-
Click + External Connection.
-
Enter the following values:
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter a unique name to identify this connection to VGW.
Connect Public Cloud To
-
Select the CSP Gateways radio button.
-
Click on the dropdown menu and select AWS VGW.
Local Gateway
Enter the name of the Transit Gateway to connect to VGW.
Local ASN
Enter the BGP AS number the Transit Gateway will use to exchange routes with VGW.
VGW Account Name
Enter the name of this AWS account that VGW is created with.
VGW Region
Enter this AWS region where VGW is created.
VGW ID
Enter the VGW that is created in the VGW Region in the AWS account.
Learned CIDR Approval
This is Off and disabled by default unless the Local Gateway you select has Learned CIDR Approval turned On; the Connection option selected, and the BGP connection selected. Then it is On by default (not editable).
-
-
Click Save.
The new AWS VGW connection appears in the table.
The Aviatrix Transit Gateway can connect to a VGW that belongs to a different AWS account in a different region.
It takes a few minutes for the VPN connection to come up and routes from VGW to be propagated. When the IPsec tunnel with a VGW is up, the Controller admin should receive an email notification.
If you log in to the AWS Console and select service VPC in the region where the VGW is, you should see that the Customer Gateway and VPN Connections have been created. Do not delete or modify them from AWS Console. These resources are deleted if you disconnect the VGW.
Checking Route Propagation
You can check if routes are properly propagated.
-
Go to Diagnostics > Cloud Routes > BGP Info.
-
In the table, next to the name of the Transit Gateway used in the above external connection.
-
Click the vertical ellipsis
 and select Show BGP Learned Routes to display the total number and list of routes propagated from the VGW.
and select Show BGP Learned Routes to display the total number and list of routes propagated from the VGW.
Checking Tunnel Status
You can check the tunnel connection between the AWS VGW and the Transit Gateway from Diagnostics > Cloud Routes > BGP Info. Expand the Transit Gateway in the list and check that the Status column shows Established.
If some external connections for the selected Transit Gateway are Not Established, the overall BGP Status for the Transit Gateway is Partially Established.